Many health-conscious individuals are confused about the role of dietary fat in their diet. Ever since the low-fat craze of the 80s and 90s, many Americans think the best way to reduce the risk of heart disease and obesity is to follow a low-fat diet. This is because the overall thinking of that time was that fat was more calorically dense than either carbs or protein, so it made sense it would lead to weight gain and heart disease. That’s why so many individuals opted for fat-free cookies (SnackWells, anyone?) and sugary gummies instead of wholesome foods with fat like nuts, seeds, and full-fat dairy products. The problem? As it turns out, there wasn’t sufficient scientific evidence to support a low-fat diet for health and longevity.
Fast-forward several decades and health professionals all agree that it’s the type of fat—not the amount of fat—that matters for health and reducing risk for chronic conditions. Foods that contain fat provide essential fatty acids that play an important role in the health of your brain, heart, eyes, and immunity. Dietary fat is also essential for digestion and absorption of fat-soluble nutrients like vitamins A, D, E, and K and myriad fat-soluble phytonutrients. What’s more, fat is digested slowly do it enhances feelings of fullness. Being satiated post-meals can help prevent overeating and make it easier to eat with our hunger and fullness cues. Some healthy fats, in fact, can help you maintain a healthy body weight, and reduce the risk of heart disease, diabetes, certain cancers, dementia, and much more.
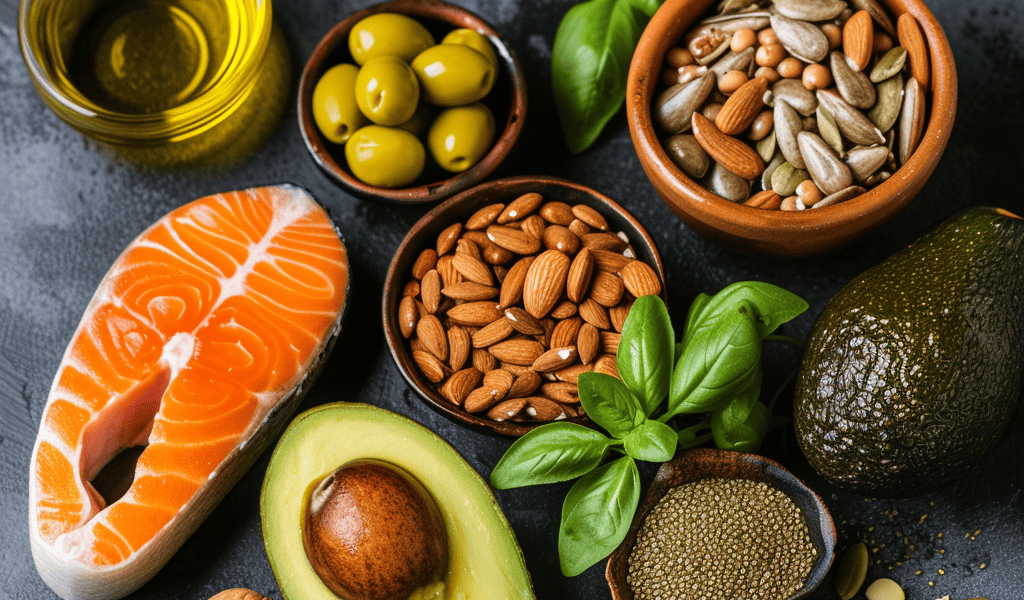
The 10 Best Healthy Fat Foods
Here’s a look at the 10 best sources of healthy fats, all backed by science.
Olive Oil
Olive oil has likely more research than any other oil regarding its health and nutritional benefits. It is a key staple in the Mediterranean diet, considered one of the healthiest ways to eat to add more years to your life. Olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats, and extra virgin olive oil in particular, provides