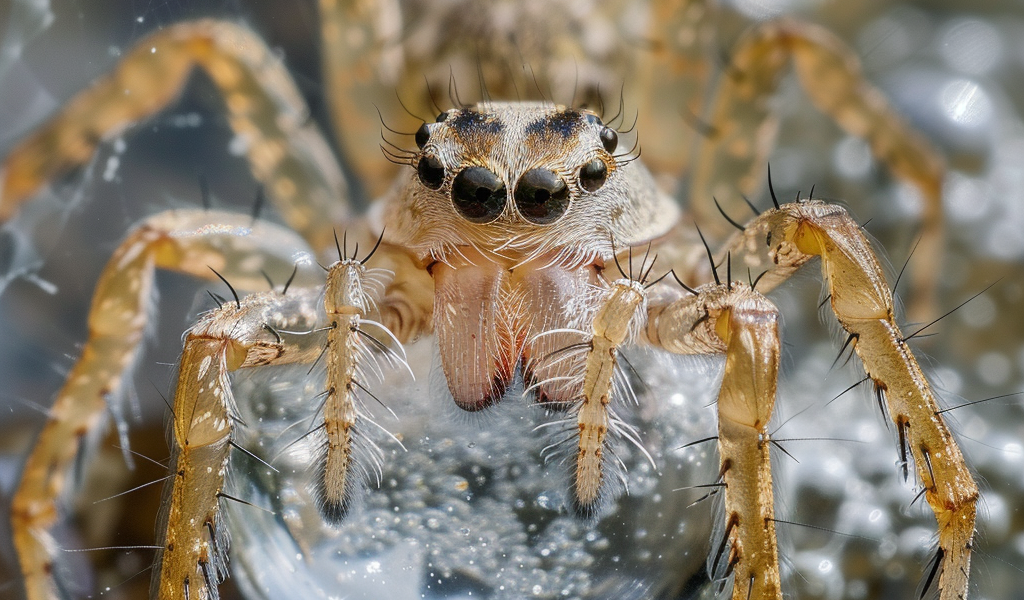
Diving bell spiders are fascinating creatures that have captured the attention of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. These unique arachnids, also known as water spiders (Argyroneta aquatica), are the only spiders that live almost entirely underwater. Found in Europe, Central and Northern Asia, as well as in Japan, these remarkable spiders have developed an extraordinary adaptation for their aquatic lifestyle.
One of the most remarkable features of the diving bell spider is its ability to create a diving bell, a structure that allows it to breathe underwater. Using its water-repellent hairs, the spider traps air from the water’s surface and spins a silk structure to form an air bubble, which it uses as a diving bell. The spider then expands the bubble until it can fit inside, carrying a bubble of water around with it, giving it a silvery coloration.
Interestingly, female diving bell spiders build larger air bells compared to males, as they need the extra space to serve as a nursing chamber for their young. This unique behavior sets them apart from other spider species and showcases the remarkable adaptations that have evolved in these aquatic arachnids.
Male diving bell spiders, on the other hand, exhibit an unusual characteristic for spiders – they are larger and heavier than females. A study published in the journal Evolutionary Ecology Research in 2003 explored the reasons behind this phenomenon. The research revealed that larger size and longer front legs in males allowed for more efficient movement underwater, providing insights into the unique adaptations of these fascinating creatures.
Despite their captivating traits, diving bell spiders also exhibit peculiar behavior when it comes to reproduction. Males have been observed engaging in reverse sexual cannibalism, occasionally consuming females. This behavior adds another layer of complexity to the already intriguing world of diving bell spiders.
With their remarkable ability to thrive in aquatic environments and their distinctive behaviors, diving bell spiders continue to fascinate researchers and nature enthusiasts. As scientists delve deeper into the mysteries of these underwater arachnids, the unique adaptations and behaviors of the diving bell spider are sure to captivate the curiosity of many for years to come.