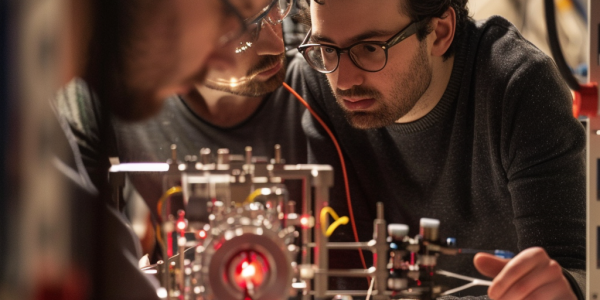
Breakthrough in Quantum Computing with Microwave Circulator Device
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have made a groundbreaking discovery in quantum computing with the development of a microwave circulator. This device allows precise control of nonreciprocity between qubits and microwave-resonant cavities, essential for quantum information processing. Their research, published in Science Advances, introduces a new theory that simplifies and enhances previous understandings of nonreciprocity, benefiting future studies in the field. Quantum computing, based on qubits in quantum superposition, offers enhanced computational power, while nonreciprocity opens up new possibilities for harnessing the full potential of the quantum realm.
Groundbreaking Robotic Hip Exoskeleton for Stroke Recovery
A recent study by the University of Massachusetts Amherst introduces a portable robotic hip exoskeleton designed to improve walking function in stroke survivors. With over 80% of stroke patients experiencing walking difficulties, this innovation holds promise in significantly enhancing their daily lives and overall quality of life. The research highlights the potential of the robotic hip exoskeleton to effectively train individuals to modify their walking asymmetry, offering a new avenue for stroke rehabilitation.
UMass Amherst Study Finds Dried Fruit to be Healthiest Fruit Snack Option
UMass Amherst researchers have found that fruit gummies are the least nutritious fruit snack, with dried fruit being the healthiest option. Their analysis of nearly 1,500 fruit snacks revealed that dried fruit, pureed fruit, and canned fruit with juice met the latest high-nutrition snack recommendations, while gummies and other sugary options fell short.