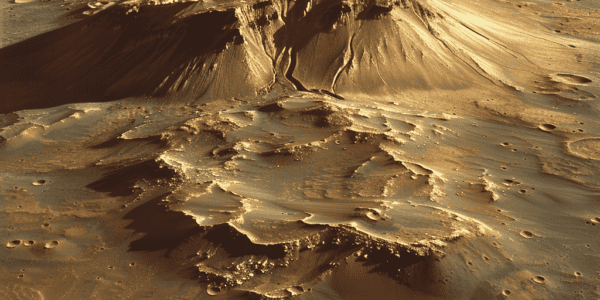
Giant Volcano and Possible Glacier Ice Discovered on Mars
A giant volcano and possible buried glacier ice have been discovered in the eastern part of Mars’ Tharsis volcanic province, near the planet’s equator. This groundbreaking announcement was made at the 55th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference in Texas, revealing that the giant volcano, provisionally designated “Noctis volcano,” had been hiding in plain sight for decades. The discovery of this giant volcano and potential glacier ice points to an exciting new location to study Mars’ geologic evolution through time and search for signs of life. The structure’s gigantic size and complex modification history indicate that it has been active for a very long time, from ancient through recent times. This finding opens up new possibilities for future exploration and research on Mars.
The Search for the Origin of Life on Earth
The search for the origin of life on Earth has captivated scientists for years. With various theories and hypotheses, researchers are exploring how life could have emerged on a hot and rocky planet like Earth. One popular theory involves the early Earth’s atmosphere, dominated by nitrogen and methane, which could efficiently produce organic compounds. The famous Miller-Urey experiment simulated these conditions and yielded astonishing results, suggesting that lightning, asteroid impacts, and ultraviolet radiation from the Sun could have combined to create the necessary chemicals for life.
Scientists Discover Remarkable Planetary System 100 Light-Years Away
Scientists have discovered a remarkable planetary system around 100 light-years from our Solar System, hailed as the most mathematically perfect system of exoplanets ever observed. The star at the center, an orange dwarf named HD 110067, is orbited by six exoplanets that move in perfect harmony, intriguing scientists with the potential for life and the search for alien technology.
Unusual Fluctuations in Jupiter’s Magnetic Field
Unusual fluctuations in Jupiter’s magnetic field could reveal secrets about the gas giant’s core. Scientists from Harvard University observed changes in the magnetic field, indicating the presence of mysterious waves deep inside Jupiter. These fluctuations, concentrated in the ‘Great Blue Spot’, suggest the presence of waves in the metallic core, potentially unlocking the forces governing Jupiter’s magnetic field.
Groundbreaking Discovery Challenges 200-Year-Old Law of Physics
Groundbreaking discovery challenges 200-year-old law of physics governing heat diffusion in solid materials. Recent research on the nanoscale shows that Fourier’s law does not accurately predict heat diffusion in these materials. Researchers at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, investigate exceptions to Fourier’s law at the macroscale, particularly in translucent materials. This discovery has significant implications for our understanding of heat diffusion in solid materials and could pave the way for new advancements in thermal conductivity research.
Discovery of 18 New Species of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
Researchers have discovered 18 new species of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, shedding light on the origins of antibiotic resistance and potential insights into curbing these infections. The findings aim to enhance understanding of how resistance genes spread to hospital bacteria, posing a threat to human health. The research team collected samples from remote regions worldwide, including penguins in sub-Antarctic waters, duiker and elephants in Uganda, insects, bivalves, sea turtles, and wild turkeys in Brazil and the United States, kestrel and vultures in Mongolia, wallaby, swans, and wombats in Australia, as well as zoo animals and wild birds in Europe.
Scientists Investigate Drying out the Stratosphere to Reduce Warming
Scientists are exploring the feasibility of removing water vapor from the stratosphere as a means of reducing global warming. While this approach could have a cooling effect, it would not be enough to counteract the significant warming from carbon dioxide emissions. The study outlines technical barriers and the need for more measurements to better understand the distribution of water in the atmosphere.
Scientists Want to Lay Fiber Optic Cable on the Moon
Seismologists are exploring the idea of deploying a fiber seismic network on the Moon to detect quakes on the lunar surface. They want to know what triggers these events and have a plan in the works. With the Artemis mission picking up pace, the prospect of laying fiber optic cable on the Moon could soon become a reality.
Researchers Develop First Synthetic Molecular Motor ‘The Lawnmower’
Researchers at Simon Fraser University and Lund University have created the first synthetic molecular motor, ‘The Lawnmower,’ capable of propelling itself by harnessing the energy it generates as it cuts through fields of proteins. This groundbreaking achievement has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of various diseases and opens up new possibilities in the field of synthetic biology and molecular engineering.
Revolutionary ‘Artificial Leaf’ Technology Converts Solar Energy into Hydrogen Fuel
Scientists have unveiled a revolutionary ‘artificial leaf’ technology that converts solar energy into hydrogen fuel through direct water splitting. This innovative approach offers enhanced efficiency, cost-effective production, and global implications for sustainable energy solutions. The use of recyclable materials and low-melting-point metals points to a cost-effective and scalable approach for manufacturing solar energy conversion devices, potentially revolutionizing energy systems worldwide.