Clone Robotics Launches Revolutionary Humanoid Robot: Clone Alpha
Clone Robotics has unveiled the Clone Alpha, a groundbreaking humanoid robot designed for service and hospitality. With only 279 units available, this advanced robot features a unique ‘Telekinesis’ training platform and state-of-the-art technology that mimics human functionality. Pre-orders begin in 2025, marking a significant milestone in humanoid robotics and the integration of robots into everyday life.
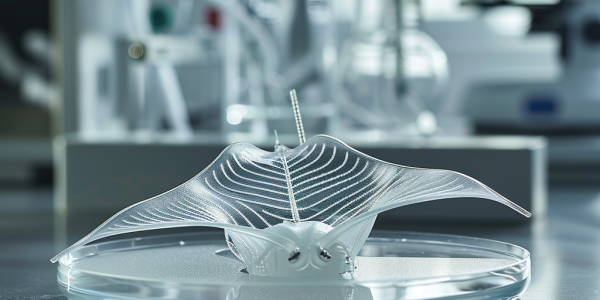
Groundbreaking Biohybrid Robot Mimics Ray Movement Using Human Muscle Tissue
A revolutionary biohybrid robot, developed by researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the iPrint Institute, mimics the swimming motion of a ray using human-derived muscle tissue. This miniature robot showcases advanced control through motor neurons and Wi-Fi technology, paving the way for innovative applications in healthcare and environmental monitoring. Published in Science Robotics, this research highlights the future of biohybrid systems in robotics and the synergy between biology and technology.
TU Delft Develops Ant-Inspired Navigation System for Micro Drones
Researchers at TU Delft have developed a groundbreaking micro-drone that mimics ant navigation strategies, enhancing its autonomous capabilities for tasks like search and rescue, environmental reconnaissance, and agricultural pollination. This innovative approach leverages odometry to improve navigation in complex environments, significantly reducing memory requirements and paving the way for future advancements in drone technology.
Study Shows Audio Data Enhances Robot Learning Capabilities
A recent study by Stanford University and Toyota Research Institute shows that incorporating audio data alongside visual data during robot training can significantly enhance learning capabilities. By equipping robots with microphones to capture audio feedback, researchers found that robots could better understand and learn tasks effectively. The study conducted four experiments, demonstrating that audio cues led to improvements in speed and accuracy of task completion. Combining audio and visual data in robot training shows potential for enhancing learning efficiency and task performance.
Flexiv Revolutionizes Car Seat Production with Automated Ironing System
Flexiv revolutionizes car seat production with automated ironing system using Rizon 4 robot. The system ensures precise material placement and consistent pressure, enhancing quality and efficiency. By automating the process, Flexiv improves workplace safety and allows employees to focus on more rewarding tasks. Future enhancements include AI visual detection for quality assurance. Flexiv’s commitment to supporting manufacturers in meeting production targets in luxury electric vehicle market.
Apple Rumored to Be Working on Revolutionary Smart Home Robot Project
Apple is rumored to be working on a new project that could revolutionize the smart home industry with robotics technology. Overseen by John Giannandrea, a former Google executive, Apple’s robotics projects are sparking speculations about the tech giant’s next big venture. While a humanoid Apple robot may still be a decade away, simpler concepts like a smaller robot or a robotic arm with a large iPad display are on the horizon. The challenge lies in designing a mobile robot that can navigate a household environment seamlessly, raising questions about functionality and form factor. Apple’s approach seems to focus on creating charming and user-friendly robots, aligning with the trend in smart home innovations like Samsung’s ‘Bot Handy.’ The future of smart home robots holds promise for enhancing daily tasks and interactions, but the journey to a fully functional household robot remains intriguing for tech enthusiasts and consumers.
Growth Expected in Robotics and Automation Actuators Market by 2032
The Robotics and Automation Actuators Market is projected to reach $45.2 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.2%. These devices play a crucial role in robotic and automated systems, enabling precise control of movement, application of force, and execution of specific tasks with accuracy and efficiency. Various types of actuators are available, each offering unique capabilities based on their energy source, including hydraulic, pneumatic, electric, piezoelectric, and magnetic actuators.
MOONS’ Industries Expands Presence in UK with High-Performance Motors for Robotics
MOONS’ Industries expands its presence in the UK, offering high-performance motors tailored for automation and robotic applications. From slotless micro motion motors for precise control in humanoid robotics to frameless motor technology for compact spaces, MOONS’ motors deliver innovative solutions for advanced robotic systems.
Comau to Showcase Latest Digital-Driven Technology at Automate 2024 Event in Chicago
Comau, a global technology company, is set to showcase its latest digital-driven technology at the upcoming Automate 2024 event in Chicago. The event will feature Comau’s cutting-edge automation solutions designed to accelerate deployment, enhance quality, and ensure sustainable productivity within smart factory environments. Comau’s exhibition will revolve around the theme of the ‘Power of Automation’, reflecting the company’s vision for the future. Attendees can expect to experience perception-guided picking systems, vision-backed handling solutions, advanced arc welding systems, and wearable robotics aimed at improving operator well-being. Comau’s participation at Automate 2024 underscores its commitment to driving the future of automation through groundbreaking technologies that offer enhanced efficiency, productivity, and quality across industrial operations.
Groundbreaking Robotic Hip Exoskeleton for Stroke Recovery
A recent study by the University of Massachusetts Amherst introduces a portable robotic hip exoskeleton designed to improve walking function in stroke survivors. With over 80% of stroke patients experiencing walking difficulties, this innovation holds promise in significantly enhancing their daily lives and overall quality of life. The research highlights the potential of the robotic hip exoskeleton to effectively train individuals to modify their walking asymmetry, offering a new avenue for stroke rehabilitation.