Physicists at CERN Discover Resonant ‘Ghost’ Force in Super Proton Synchrotron
Physicists at CERN have made a groundbreaking discovery, identifying a previously undetected force within the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS). Published in the journal Nature Physics, the research unveils the existence of a 3D shape that shifts over time, requiring a 4D system of equations for accurate measurement and modeling. The discovery of the resonant ghost is crucial for future work at the facility, shedding light on the intricate dynamics at play within particle accelerators.
Breakthrough Experiment Creates Quantum Tornado in Superfluid Helium, Offers New Insights into Black Holes
University of Nottingham physicists have created a quantum tornado in superfluid helium, offering new insights into black hole behavior. The experiment provides unprecedented precision in studying the gravitational environment of black holes and represents a significant step forward in astrophysics.
Neutron Star Mergers Shed Light on Dark Matter
Neutron star mergers provide new physics signals that could shed light on dark matter, according to a study by Washington University in St. Louis. The study, led by physicist Bhupal Dev, establishes constraints on axion-like particles using observations from the 2017 neutron star merger event, GW170817. These particles are prime candidates for constituting dark matter and could bridge the gap between the visible and dark sectors of the universe.
Groundbreaking Discovery Challenges 200-Year-Old Law of Physics
Groundbreaking discovery challenges 200-year-old law of physics governing heat diffusion in solid materials. Recent research on the nanoscale shows that Fourier’s law does not accurately predict heat diffusion in these materials. Researchers at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, investigate exceptions to Fourier’s law at the macroscale, particularly in translucent materials. This discovery has significant implications for our understanding of heat diffusion in solid materials and could pave the way for new advancements in thermal conductivity research.
Research Reveals Record-breaking Speed of Glacier Fracture in Antarctica
Recent research from the University of Washington reveals an 80-mph speed record for glacier fracture in Antarctica. The study underscores the critical need to understand the behavior of ice shelves in the face of warmer oceans and the potential implications for rising sea levels. The research has significant implications for understanding the potential impact of glacier fracture on rising sea levels and calls for further investigation into the behavior of ice shelves in large-scale ice sheet models.
Mysterious New Form of Magnetism Confirmed
Discover the confirmation of a new form of magnetism, altermagnetism, that sits between ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism. This fundamental discovery could have significant implications for future electronics and is based on the characteristic of quantum objects called spin.
Physicists Make Groundbreaking Discovery in Study of H2+ Molecule
Physicists from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) have made a groundbreaking discovery in the study of the simplest molecule, H2+. The molecule, which is composed of two hydrogen nuclei and one electron, has long been a subject of interest for astrophysics and fundamental physics due to its significance in the early formation of the universe. Published in Nature Physics, the study details the team’s successful measurement of the molecule’s vibrations using a laser, marking the first direct observation of such behavior. The findings closely align with theoretical predictions, shedding light on the elusive nature of H2+.
Colossal Magnetic Field Detected in Nuclear Matter
Researchers have observed the interaction between a state of matter known as a quark–gluon plasma (QGP) and a magnetic field 1000 times the strength of those on neutron stars. This observation is a step toward a better understanding of the strong nuclear force and puts limits on the possible value of the QGP’s electrical conductivity, informing models of the early Universe.
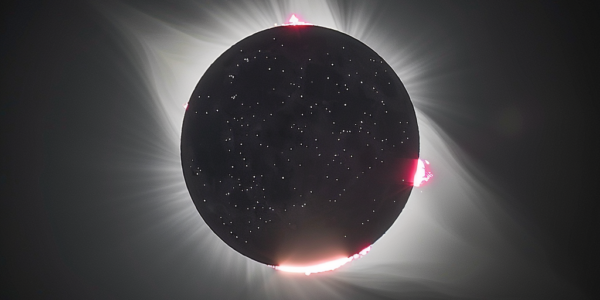
Upcoming Total Solar Eclipse to Provide New Insights into Sun’s Mysterious Corona
On April 8, 2024, a 115-mile-wide strip of North America will be plunged into darkness as the moon slips in front of the sun, creating a rosy, fluffy crown of flame visible from Mazatlán, Mexico, to Newfoundland, Canada. This upcoming total solar eclipse is generating excitement not only among spectators but also among scientists eager to study the solar corona, the mysterious outer atmosphere of the sun. The solar corona has long been a subject of fascination and mystery for astronomers, and the upcoming eclipse, along with new sun probes, is poised to revolutionize our understanding of the sun and its enigmatic corona.
Scientists Capture Movement of Electrons in Real-Time Within Liquid Water
Scientists have captured the movement of electrons in real-time within liquid water, providing unprecedented insights into the electronic structure of molecules in the liquid phase. This groundbreaking experiment sheds light on the effects of radiation exposure and holds promise for understanding the effects of prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation on nuclear waste.