New Predatory Amphipod Species Discovered in Atacama Trench
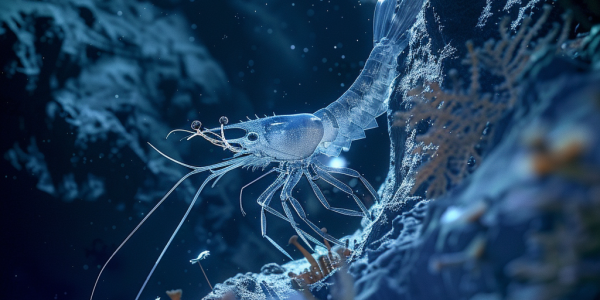
Scientists have discovered a new species of large predatory amphipod, Dulcibella camanchaca, at a depth of 25,900 feet in the Atacama Trench. This shrimp-like creature is notable for being the first known large predator in the extreme depths of the ocean, showcasing the rich biodiversity and ecological complexities of hadal zones. The discovery, made during the 2023 IDOOS Expedition, enhances our understanding of deep-sea ecosystems and the adaptations of life in harsh environments.
Groundbreaking Discovery: ‘Dark Oxygen’ Generated by Metallic Nodules in Pacific Ocean
Researchers have discovered a groundbreaking phenomenon in the Pacific Ocean, where polymetallic nodules generate oxygen in total darkness, challenging traditional beliefs about life on Earth. This study highlights the ecological implications of mining in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone, emphasizing the need for careful environmental consideration as valuable resources are extracted from the ocean floor.
AI Mapping Reveals Seafloor Invertebrate Activities Worldwide
Scientists from the U.S. and the U.K. have used AI to map seafloor invertebrate activities, shedding light on the importance of marine sediments in global ecosystems. The study, led by Texas A&M University, University of Southampton, and Yale University, provides valuable insights into ocean health and climate change responses.
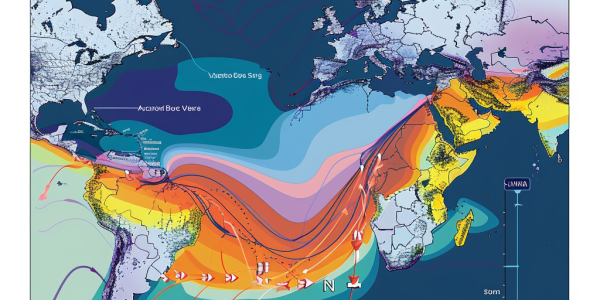
Study Reveals Weakening of Atlantic Abyssal Limb in North Atlantic
A recent study published in Nature Geoscience reveals a weakening of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation abyssal limb in the North Atlantic, impacting heat and carbon redistribution. The study shows a decrease in the transport of Antarctic Bottom Water towards the north, with warming trends contributing to sea-level rise in the region. This weakening is linked to reduced formation rates of Antarctic Bottom Water and abyssal warming in the western Atlantic Ocean.
Altering Wastewater to Slow Climate Change
A study suggests that adding alkaline chemicals to wastewater discharged into the oceans could increase CO2 sequestration, potentially mitigating climate change. This approach aims to reduce acidity of wastewater and remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, offering a sustainable method to lower CO2 levels.