Collaborative Oceanographic Research Key to Understanding Climate Change
In the next two decades, physical oceanography will focus on the ocean’s critical role in climate dynamics, emphasizing collaboration between oceanographers and meteorologists. This research is vital for understanding ocean-atmosphere interactions and developing advanced climate models to address the challenges of climate change.
Study Reveals Impact of Historical Extreme Heat on Ocean Circulation
A recent study by the University of California, Riverside reveals how historical extreme heat events impacted ocean circulation, affecting the global conveyor belt that redistributes heat and stores carbon. The findings, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, highlight the crucial role of oceans in regulating Earth’s climate and sequestering carbon dioxide. Understanding past climate events can provide insights into the future impacts of continued carbon emissions on climate stability.
Study Reveals Impact of Weakening Ocean Current on North Atlantic Ocean Life During Climate Change
Groundbreaking study reveals the impact of a weakening ocean current on North Atlantic ocean life during prehistoric climate change. Changes in ocean circulation could lead to a decline in nutrients, impacting marine ecosystems. Research provides insights into past changes in ocean currents and their effects on biological productivity. Study published in Science highlights the significance of understanding and addressing changes in ocean currents to mitigate climate change impact on marine ecosystems.
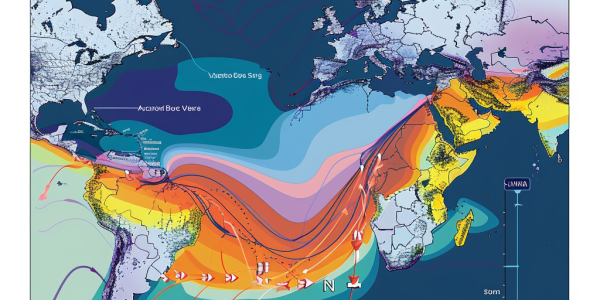
Study Reveals Weakening of Atlantic Abyssal Limb in North Atlantic
A recent study published in Nature Geoscience reveals a weakening of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation abyssal limb in the North Atlantic, impacting heat and carbon redistribution. The study shows a decrease in the transport of Antarctic Bottom Water towards the north, with warming trends contributing to sea-level rise in the region. This weakening is linked to reduced formation rates of Antarctic Bottom Water and abyssal warming in the western Atlantic Ocean.
Mars influencing Earth’s deep oceans with ‘giant whirlpools,’ scientists say
New research suggests that Mars may be influencing deep ocean currents on Earth, leading to the formation of ‘giant whirlpools.’ Scientists analyzed sediments to look back tens of millions of years into Earth’s past, revealing 2.4 million-year climate cycles linked to the interactions of Mars and Earth orbiting the Sun. This phenomenon, known as ‘resonance,’ affects the shape of their orbits and translates to periods of increased solar energy and warmer climate on Earth, correlating with more vigorous ocean currents. However, these natural climate cycles are not linked to the rapid heating the world is experiencing today due to human activities. The study’s findings provide valuable insights into the forces driving deep ocean currents and their impact on the Earth’s climate.
Atlantic Ocean Current System Showing Early Signs of Collapse, Study Finds
A new report suggests that the critical Atlantic Ocean current system is showing early signs of collapse, raising concerns among scientists about potential implications for sea level rise and global weather patterns. The findings, published in the journal Science Advances, indicate that the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), which includes the Gulf Stream, is at risk of faltering as a result of climate change.