Cygnus Spacecraft Launch Postponed Due to Weather, Rescheduled for August 4
The launch of Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft to the ISS has been postponed to August 4, 2024, due to adverse weather conditions influenced by Tropical Cyclone Four. Originally scheduled for July 30, the mission aims to deliver over 8,200 pounds of supplies and scientific equipment. As preparations continue, space enthusiasts eagerly await updates on the weather and the rescheduled launch, which is crucial for ongoing research in microgravity.
US Space Force to Establish Orbital Filling Stations for Satellite Refueling
The US Space Force is looking to establish orbital filling stations for its satellites, aiming to extend their mission life by refueling them in orbit. Northrop Grumman’s Passive Refueling Module (PRM) has been selected by the Space Force as the preferred model to set the standard for refueling satellites in orbit within the Space Systems Command (SSC). Satellites, with their high construction and launch costs, require propellant to function. Despite efforts to maximize their lifespan, the need for propellant remains a limiting factor. Many satellites require propellant to maintain their orientation, adjust orbits, and ensure operational efficiency. As a result, after a few years, satellites can become obsolete due to fuel depletion, despite being in good condition. To address this issue, companies like Northrop Grumman have been developing in-orbit servicing modules. These robotic spacecraft can dock with satellites running low on fuel, providing them with supplemental propulsion, new power sources, and even conducting minor repairs. The Space Force is particularly interested in this technology, as military satellites require frequent orbital shifts for various operational needs, making propulsion a critical asset. Refueling satellites in orbit presents challenges, requiring standardization to ensure compatibility between servicing modules and visiting satellites. This need for standardization has been a longstanding issue in space exploration, dating back to the Apollo Soyuz mission in 1975, which required a common docking mechanism for US and USSR spacecraft. The development of orbital filling stations and standardized refueling technology holds promise for extending the operational lifespan of satellites, offering a cost-effective solution for maintaining and enhancing satellite capabilities in orbit.
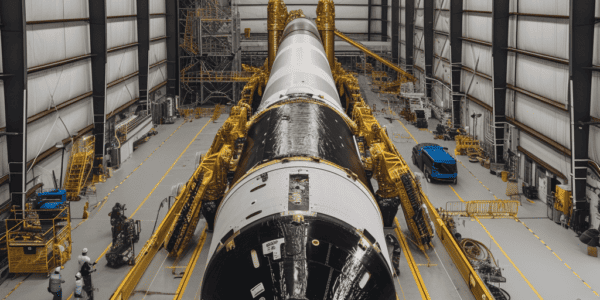
Cygnus Cargo Spacecraft Set to Launch on Falcon 9 Rocket for the First Time
A Cygnus cargo spacecraft is set to launch on a Falcon 9 rocket for the first time, marking a significant milestone in space exploration. The mission, designated NG-20, is scheduled to lift off from Cape Canaveral’s Space Launch Complex 40…