Study Reveals Protein Role in Aging-Related Cognitive Decline
A recent study published in Nature Communications reveals that protein buildup in aging fruit flies parallels human memory loss. Researchers found that filamentous actin (F-actin) accumulation impairs brain function, but genetic modifications can prevent this buildup, extending lifespan by 30%. This research offers insights into cognitive decline and potential interventions for enhancing cognitive health in aging populations.
Revolutionary Prenatal Gene Editing Method Shows Promise for Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Researchers from UC Davis and UC Berkeley have developed a groundbreaking method for prenatal gene editing using acid-degradable nanoparticles. This innovative technique targets neurodevelopmental disorders by delivering mRNA into embryonic brain cells, achieving significant genetic modifications with low toxicity. Published on October 28, 2024, the study highlights a promising approach to treat genetic disorders before birth, potentially revolutionizing therapies for conditions like Angelman syndrome and Rett syndrome.
Groundbreaking Study Reveals Brain Structure Differences in Children with Autism
Recent research from the University of Rochester reveals critical structural differences in the brains of children with autism, highlighting lower neuron density in key cerebral regions. This groundbreaking study paves the way for enhanced diagnostic methods and targeted treatments, offering new insights into autism’s neurological foundations. Published in Autism Research, the findings could lead to more personalized interventions for affected children.
Navigating Privacy and Breakthroughs in Multiple Sclerosis Research
In today’s digital age, understanding privacy choices is crucial as users navigate online platforms. Essential cookies ensure basic functionality, while optional cookies enhance user experience but may involve data sharing with third parties. Recent research in regenerative medicine highlights a groundbreaking study on CRISPR-edited cells that could improve remyelination in Multiple Sclerosis, offering hope for new treatments. Stay informed about your online privacy and the latest scientific advancements.
Study Reveals SOD1 Trimer’s Role in ALS Progression
A groundbreaking study from Penn State College of Medicine reveals critical insights into the toxic protein SOD1 and its role in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Published in the journal Structure, the research highlights how SOD1 trimers uniquely interact with brain, spinal cord, and muscle tissues, influencing neurodegenerative processes and cellular functions. This study paves the way for potential therapeutic targets, particularly focusing on the interaction between SOD1 trimers and septin-7, offering hope for new ALS treatments.
Advancements in Neuroscience: New Insights from Drosophila Research
In the digital age, privacy is crucial for users on online platforms. Organizations use essential cookies for website functionality, while optional cookies enhance advertising and personalization. Users can manage cookie preferences to protect their data. Additionally, recent neuroscience advancements highlight the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, in a groundbreaking study that identifies 8,453 distinct cell types, refining our understanding of neuronal diversity and connectivity.
Research Links Swallowing Mechanism to Binge Eating
Recent research from the University of Bonn reveals a crucial link between swallowing and overeating, suggesting that the act of swallowing may drive our desire to eat more by releasing serotonin, the ‘feel-good’ hormone. This study, which utilized fruit fly larvae to explore eating behaviors, highlights the importance of both physiological and psychological factors in managing eating habits and addressing issues like binge eating and anorexia. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to innovative strategies for promoting healthier eating patterns.
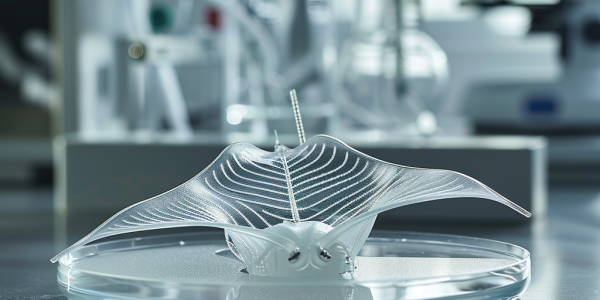
Groundbreaking Biohybrid Robot Mimics Ray Movement Using Human Muscle Tissue
A revolutionary biohybrid robot, developed by researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the iPrint Institute, mimics the swimming motion of a ray using human-derived muscle tissue. This miniature robot showcases advanced control through motor neurons and Wi-Fi technology, paving the way for innovative applications in healthcare and environmental monitoring. Published in Science Robotics, this research highlights the future of biohybrid systems in robotics and the synergy between biology and technology.
Revolutionary Neurotechnology Promises Breakthroughs in Brain Mapping and Treatment
Scientists at the Salk Institute have unveiled a revolutionary neurotechnology called Single Transcriptome Assisted Rabies Tracing (START), enabling unprecedented mapping of neuronal connections in the brain. This innovative tool combines monosynaptic rabies virus tracing with single-cell transcriptomics to identify distinct neuronal subtypes, particularly inhibitory neurons, in the cerebral cortex. The implications for targeted treatments for neurological conditions like autism and schizophrenia are profound, paving the way for more effective and individualized therapies.
Understanding Digital Privacy and Drug-Induced Cognitive Deficits
Explore the crucial insights into digital privacy and data consent, alongside groundbreaking research on cognitive deficits linked to drug use. Understand how drug exposure alters brain function and the potential for targeted therapies to reverse memory impairments. Stay informed about the implications of your data choices and the latest in substance use research.