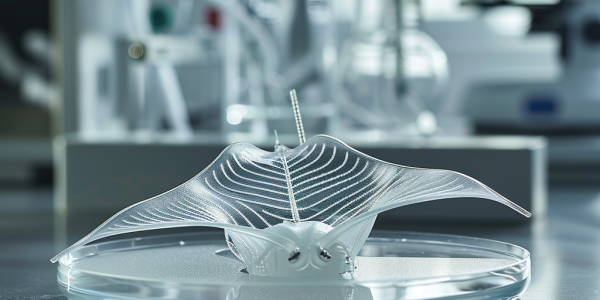
Groundbreaking Biohybrid Robot Mimics Ray Movement Using Human Muscle Tissue
A revolutionary biohybrid robot, developed by researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the iPrint Institute, mimics the swimming motion of a ray using human-derived muscle tissue. This miniature robot showcases advanced control through motor neurons and Wi-Fi technology, paving the way for innovative applications in healthcare and environmental monitoring. Published in Science Robotics, this research highlights the future of biohybrid systems in robotics and the synergy between biology and technology.
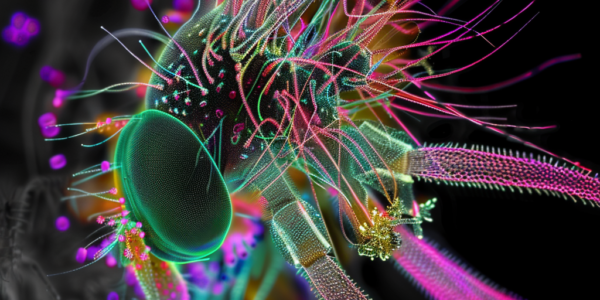
Unlocking Motion: The Unexpected Complexity of Motor Neurons
Researchers have challenged traditional views on motor neurons through a groundbreaking study on fruit flies, demonstrating that individual motor neurons can produce a variety of complex head movements rather than just simple actions. This research highlights the intricate role these neurons play in bodily motion and opens new avenues for understanding motor system diseases and the interplay between different types of neurons in movement control.