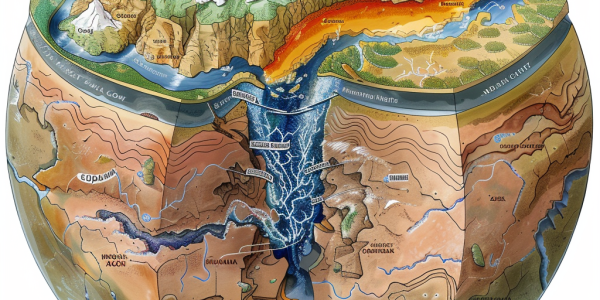
New Model Reveals Deformation Mechanisms of North China Craton
A recent study published in Nature Geoscience reveals the geodynamic mantle-flow model explaining the deformation of the North China Craton (NCC). Led by Professor Shaofeng Liu, the research uncovers the impact of the Izanagi plate’s subduction on NCC’s decratonization, offering insights into tectonic interactions and implications for seismic hazards in Northeast Asia.
Ancient Zircon Discovery on Easter Island Challenges Volcanic Activity Understanding
Recent research from Colombia’s Universidad de Los Andes reveals that zircon minerals on Easter Island date back 165 million years, challenging existing geological timelines. Led by geologist Yamirka Rojas-Agramonte, this groundbreaking study suggests a more complex history of volcanic activity and Earth’s mantle dynamics, reshaping our understanding of hotspot volcanoes and their formation.
New Research Challenges Stability of Earth’s Ancient Cratons
Recent geological studies reveal that Earth’s ancient crust, known as cratons, is undergoing significant changes, challenging long-held beliefs about their stability. Research on the North China Craton highlights dynamic processes leading to ‘decratonization,’ reshaping our understanding of geological stability and the evolution of Earth’s crust.
Ancient Seafloor Discovery Reshapes Understanding of Earth’s Interior
Recent research from the University of Maryland has uncovered an ancient seafloor beneath the Pacific Ocean, reshaping our understanding of Earth’s interior. Utilizing advanced seismic imaging, scientists revealed a thickened area in the mantle transition zone, providing insights into geological processes like subduction. This groundbreaking study, led by Jingchuan Wang, highlights the potential of seismic techniques in uncovering hidden geological features and enhancing our knowledge of the Earth’s evolution.
New Research Unveils Groundbreaking Insights into Earth’s Ancient Mantle
Recent research from the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History reveals groundbreaking insights into Earth’s geological history through the study of 2.5 billion-year-old ‘time capsule’ rocks. These findings challenge long-held beliefs about the oxidation state of the Earth’s mantle, suggesting stability over geological time. This research not only enhances our understanding of Earth’s early processes but also connects to the broader narrative of life’s origins on our planet.
Remains of ‘Buried Planet’ Uncovered Deep Within Earth, Potentially Linked to Moon-Forming Impact
Scientists have made a fascinating discovery deep within the Earth, uncovering the remains of a ‘buried planet’ possibly linked to a moon-forming impact 4.5 billion years ago. Seismologists identified massive ‘basal mantle anomalies’ beneath the Pacific and Africa, suggesting a unique material composition. Researchers speculate these anomalies could be remnants of a planet named Theia, offering insights into Earth’s collision history and moon formation. The discovery opens new avenues for understanding celestial collisions and planetary dynamics.
Scientists Discover Massive Subterranean Ocean 400 Miles Underground
Recent study reveals a massive subterranean ocean 400 miles underground, challenging our understanding of the planet’s water cycle. The water is located in the mantle transition zone and was discovered through tectonic wave measurements. This challenges previous beliefs about the distribution of water within the Earth.
Earth’s Crust Flipped Upside Down Beneath Mediterranean
Earth’s crust has flipped upside down beneath the Mediterranean as Africa and Eurasia collide, leading to rare, deep earthquakes in Spain. Geologists suggest that the capsized tectonic slab may be responsible for the seismic activity. The sinking of the Mediterranean floor beneath Europe is causing the crust to become more prone to earthquakes, as explained by a new study.