Revolutionizing Financial Analysis with GPT-4
Recent research from the University of Chicago showcases the remarkable potential of GPT-4, a cutting-edge large language model, in revolutionizing financial statement analysis. With superior prediction accuracy and analytical prowess surpassing human analysts, GPT-4 offers unprecedented insights and predictive capabilities, signaling a paradigm shift in the future of financial analysis.
Slack Faces Backlash Over Use of Messages for AI Training
Slack users are concerned about their messages being used for AI training without a clear opt-out option. Despite Slack’s statement that it does not train its large language models on customer data, users are questioning the platform’s data usage policies. The discrepancy between Slack’s privacy principles and its promotion of Slack AI has caused confusion among users, leading to backlash. However, Slack has announced upcoming policy changes to address these concerns and clarify that customer data is not used to develop or train generative AI models.
Regulators Crack Down on AI Washing in Tech Industry
Federal regulators are cracking down on AI washing, where companies overstate the role of AI while relying heavily on human operators. Amazon’s ‘Just Walk Out’ technology and other companies have been found to use human intervention to power their AI systems. Regulators, including the SEC, are taking action against companies engaging in AI washing, signaling a growing awareness of the importance of transparency and accountability in the deployment of AI technologies.
The Importance of Ensuring Accessibility in the AI Future
Learn about the importance of accessibility in the AI future and how prioritizing inclusivity can create a more equitable technological landscape for all. Addressing issues of bias and discrimination in AI algorithms is crucial to ensure that the benefits of AI are distributed fairly.
Snapchat Introduces AI-Powered AR Tools for Advertisers
Snapchat introduces AI-powered augmented reality tools for advertisers, including AR Extensions for seamless integration of AR lenses and filters into various ad formats. With new machine learning and automation tools, brands can transform 2D product catalogues into interactive 3D try-on assets more efficiently. The platform also offers custom branded AR ads using generative AI technology, enhancing engagement with Snapchatters. By expanding collaborations and enhancing direct response products, Snapchat aims to empower advertisers to elevate their business and engage with consumers in immersive ways.
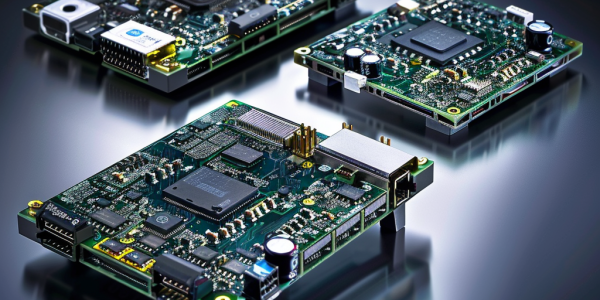
New NXP i.MX 93-Based System-on-Modules Launched by MYiR, Variscite, and Compulab
Discover the latest NXP i.MX 93-based system-on-modules launched by MYiR, Variscite, and Compulab. These modules offer advanced features for industrial, IoT, and automotive applications, with the powerful NXP i.MX 93 processor at their core. Learn about the key offerings from MYiR, Variscite, and Compulab, and how these modules are revolutionizing the embedded systems market.
Snapchat Unveils Exciting Plans for Summer Olympics at NewFronts Event
Snapchat unveils exciting plans for the upcoming Summer Olympics, including a significant investment in sports and creators. The platform will feature top stars like gymnast Livvy Dunne, reality TV star Harry Jowsey, and gamer/comedian Kai Cenat reporting from Paris. Snap also announces a collaboration with NBCUniversal to introduce new augmented reality lenses featuring Team USA athletes. The platform’s partnerships with major sports leagues like the NFL, NBA, and WNBA highlight its commitment to engaging users with compelling content and immersive experiences.
Automated Machine Learning Robot Revolutionizes Genetics Research
University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers have developed an automated machine learning robot revolutionizing genetics research. This technology enables manipulation of genetics in multicellular organisms, saving time and resources for laboratories. The innovative robot is featured in the April 2024 issue of GENETICS and is being commercialized through Objective Biotechnology. This groundbreaking technology surpasses manual injections in robustness and reproducibility, opening new possibilities for large-scale genetic experiments.
UMass Amherst Researchers Use AI to Eavesdrop on Insects for Environmental Health Assessment
UMass Amherst researchers are leveraging machine learning to eavesdrop on the insect world, aiming to enhance environmental health assessment. By identifying different insect species through their sounds, researchers hope to gain insights into the shifting populations of insects, which can provide valuable information about the overall health of the environment. The study, recently published in the Journal of Applied Ecology, highlights the increasing significance of machine and deep learning in automated bioacoustics modeling. Laura Figueroa, assistant professor of environmental conservation at UMass Amherst and the senior author of the paper, emphasizes the crucial role of insects in ecosystems and the challenges in monitoring their populations. With the rise of environmental stressors and drastic changes in insect populations, traditional sampling methods are proving to be insufficient. The collaboration between ecologists and machine-learning experts is seen as a promising approach to fully unlock the potential of AI in identifying and monitoring insect populations. The potential of AI in environmental health assessment is evident, offering a non-invasive and efficient alternative to traditional entomological methods. As Figueroa points out, the ability to differentiate insect sounds and train AI models to identify species based on their unique sounds opens up new possibilities for understanding and safeguarding insect populations in the face of environmental challenges.
AI’s Exploration of the ‘Dark Genome’ and Its Impact on Cancer Research
AI has made significant strides in cancer research by delving into the ‘dark genome’ to revolutionize our understanding of cancer and pave the way for more effective treatments. By analyzing non-coding DNA sequences with AI technology, researchers can identify potential therapeutic targets and uncover novel biomarkers for early cancer detection. This intersection of AI and the ‘dark genome’ represents a paradigm shift in cancer research, offering unprecedented opportunities to unravel the complexities of cancer biology and transform the landscape of oncology.