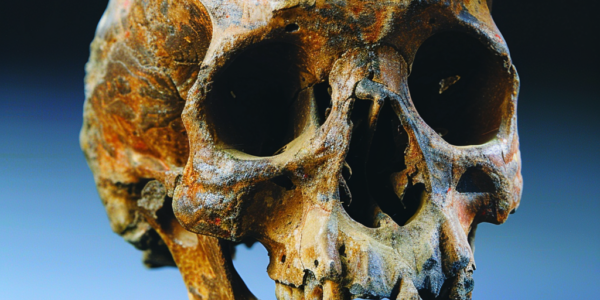
Groundbreaking Research Reveals Complex Interactions Between Modern Humans and Neanderthals
Recent genetic research reveals significant intermingling between early humans and Neanderthals, challenging long-held perceptions of these ancient groups. Led by Joshua Akey from Princeton University, the study highlights complex interactions and shared traits, suggesting Neanderthals were not merely primitive but possessed advanced skills and social behaviors. This groundbreaking work redefines our understanding of human evolution, emphasizing the interconnectedness of our ancestry.
New Study Reveals Complex Interactions Between Early Humans and Neanderthals
Recent genetic research reveals new insights into the extinction of Neanderthals and their interactions with early humans. A groundbreaking study published in Science uncovers multiple DNA exchanges over 250,000 years, challenging previous notions of human evolution and migration. This research highlights the complex relationships between different hominin species, suggesting that Neanderthals were not isolated but engaged with modern humans and other archaic species like the Denisovans. These findings reshape our understanding of human ancestry and the genetic legacy that influences us today.
Evolutionary Study Uncovers Potential Non-Addictive Pain Management Solutions
Recent study explores non-addictive alternatives for pain management by focusing on the evolution of a human protein responsible for cold sensations. By understanding the chemical sensing of cold versus physical sensation, researchers aim to develop side-effect-free pain medications, offering hope for effective relief without the risks of addiction or overdose.
Primate Chromosome Sequencing Reveals Evolutionary Insights
Scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery by generating the first complete chromosome sequences from non-human primates, shedding light on species diversity and evolution. Published in Nature, the study compared ape chromosomes to human X and Y chromosomes, revealing significant variation and uncovering previously unstudied regions of great ape genomes. The research offers valuable insights into human evolution and genetic relationships between primates and humans.
Breakthrough in Understanding the Denisovans: Link to Homo Longi
Scientists have made a significant breakthrough in understanding the mysterious Denisovans, an ancient human group that has long puzzled researchers. A recent discovery has shed light on the potential identity of the Denisovans, linking them to Homo longi, also known as ‘Dragon man,’ whose fossil was found in Harbin, northeast China. This breakthrough represents a significant advancement in the study of Denisovans, offering a potential glimpse into their appearance and lifestyle.
Ancient Stone Points Unearthed in Ethiopia
Groundbreaking discovery in Ethiopia as stone points dating back 74,000 years shed light on ancient human adaptability. The archaeological site has yielded evidence of hunter-gatherer resourcefulness and ability to thrive in changing circumstances. The findings offer valuable insights into human migration and settlement, showcasing the resilience and ingenuity of our ancestors.
Ancient Primate Ancestors’ Appetite for Soft Fruits Shaped Human Evolution
Research on early anthropoids suggests a diet high in soft fruits, with tooth decay in some individuals indicating a diet ripe and high in sugar. This has important implications for understanding how our earliest ancestors adapted and evolved. Genetic and molecular studies, along with fossil evidence, indicate the period from 40 to 25 million years ago was a critical phase for the evolution and spread of anthropoid primates.
Human Evolution and Climate Crisis
Human evolution might be the biggest threat to solving the climate crisis, according to a new study from the University of Maine. The research aimed to understand how the process of cultural adaptation to the environment, a significant driver of…
Human Evolution and Climate Change
Evolution might stop humans from solving climate change, researchers say By Marcus Wolf, University of Maine Humans have come to dominate the planet with tools and systems to exploit natural resources that were refined over thousands of years through the…