Rare Genetic Variants Linked to Left-Handedness, Study Finds
Discover the groundbreaking genetic study that unveils rare genetic variants of the TUBB4B gene as more prevalent in left-handed individuals. This research sheds light on the biological factors influencing handedness and offers valuable insights into the genetic underpinnings of this phenomenon.
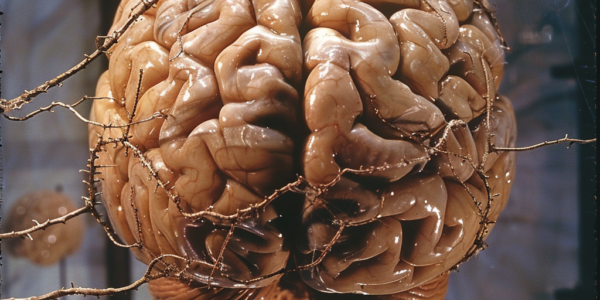
Genetic Basis of Human Handedness Revealed in New Study
A new study published in Nature Communications reveals the genetic basis of human handedness, suggesting that rare protein-altering variants may play a significant role. The study involved exome data from over 38,000 left-handed and 313,000 right-handed individuals, finding significant association with left-handedness in the beta-tubulin gene TUBB4B. The research also identified rare coding variant association with left-handedness in genes previously implicated in autism or schizophrenia, shedding light on the genetic underpinnings of this trait and offering valuable insights into the genetic factors influencing human handedness.