New Stem Cell Model Unveils Genetic Pathway of Childhood Cancer Neuroblastoma
Researchers from the University of Sheffield have made a groundbreaking discovery in the genetic pathway of neuroblastoma, a childhood cancer, leading to new possibilities for personalized treatments. By developing a stem cell model to investigate the origins of neuroblastoma, they have identified specific mutations that contribute to the development of aggressive tumors. This innovative approach offers hope for more effective and tailored treatment strategies in the future.
Study Links rDNA Copy Number to Inflammation and Disease Risk
A recent study by Queen Mary University of London found a strong association between ribosomal DNA (rDNA) copy number and the risk of inflammation and diseases. The research, analyzing samples from 500,000 individuals, highlights the potential of rDNA analysis in identifying genetic predispositions to various health issues. The findings suggest that a broader genome analysis could lead to early disease detection and innovative treatment approaches, emphasizing the importance of leveraging biobanks for improved healthcare outcomes.
Experimental Gene Therapy Restores Vision in Patients with Inherited Blindness
An experimental gene therapy has shown promising results in restoring vision for patients with inherited blindness. College student Olivia Cook underwent a CRISPR-based gene-editing treatment that significantly improved her vision, providing hope for advancements in science and vision restoration. Despite being experimental, the therapy offers hope for treating inherited retinal disorders and combating blindness worldwide.
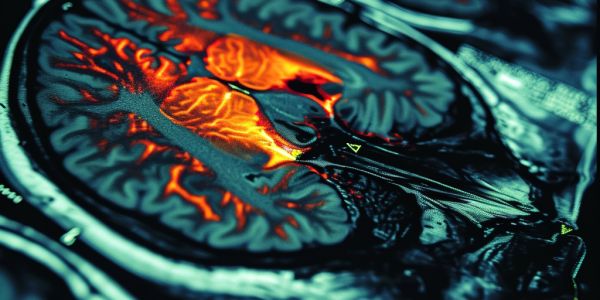
Study Reveals APOE4 Homozygosity as Distinct Genetic Form of Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study reveals that APOE4 homozygosity represents a distinct genetic form of Alzheimer’s disease, with near-full penetrance of AD biology, earlier symptom onset, and specific biomarker changes. Individualized prevention strategies and treatments are emphasized for this unique genetic profile.
Revolutionary Gene Therapy Delivery Method Developed by UW–Madison Researchers
Discover the groundbreaking method developed by researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison to enhance the delivery of gene therapies through short electric pulses, increasing uptake by over 40 times. This innovative approach could lead to safer and more accessible treatments for genetic diseases like cystic fibrosis and diabetes.
Epigenetic Mechanisms Found to Play Key Role in Cancer Development
Recent research published in Nature reveals that epigenetic mechanisms, specifically the disruption of Polycomb group proteins, can lead to cancer cell fate without genetic mutations. This challenges the traditional view of tumorigenesis and emphasizes the importance of understanding epigenetic dysregulation in cancer development and therapy.
Automated Machine Learning Robot Revolutionizes Genetics Research
University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers have developed an automated machine learning robot revolutionizing genetics research. This technology enables manipulation of genetics in multicellular organisms, saving time and resources for laboratories. The innovative robot is featured in the April 2024 issue of GENETICS and is being commercialized through Objective Biotechnology. This groundbreaking technology surpasses manual injections in robustness and reproducibility, opening new possibilities for large-scale genetic experiments.
New Gene Linked to Rare Lung Disease PCD Identified by Scientists at University of Leicester
University of Leicester scientists have identified a new gene, tubulin (TUBB4B), linked to primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), shedding light on the genetic mechanisms underlying this rare lung disease. The research, published in Science, reveals diverse clinical manifestations and the impact of mutations on tubulin protein function. This breakthrough has the potential to enhance rapid diagnostic techniques and inform new therapeutic approaches for PCD patients.
Brain Organoids: A Promising Tool for Targeting Neurological Disorders
Brain organoids, a cutting-edge technology in neuroscience, are revolutionizing the study of rare neurological disorders. These miniature 3D brain models offer researchers a unique opportunity to unravel the complexities of brain conditions. By mimicking the structure and function of the human brain, brain organoids are shedding light on the underlying mechanisms of neurological disorders and paving the way for more effective treatments.
Experts Call for Global Genomic Surveillance System to Prevent Future Pandemics
Experts are advocating for a global genomic surveillance system to prevent future pandemics by utilizing real-time sequencing to track the spread of new diseases. Whole genome sequencing is highlighted as crucial for swiftly identifying and responding to emerging health threats, as demonstrated during the COVID-19 pandemic. Universal access to real-time surveillance is emphasized as a proactive measure for global health security.