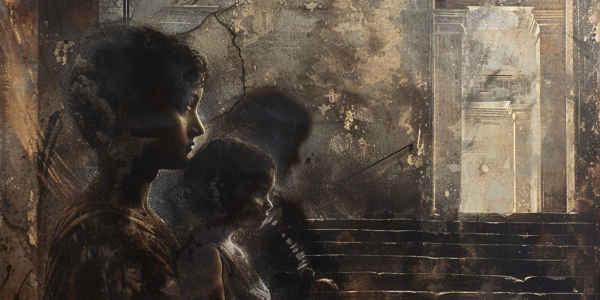Revolutionary NanoGripper Device Targets Viruses Using DNA Origami
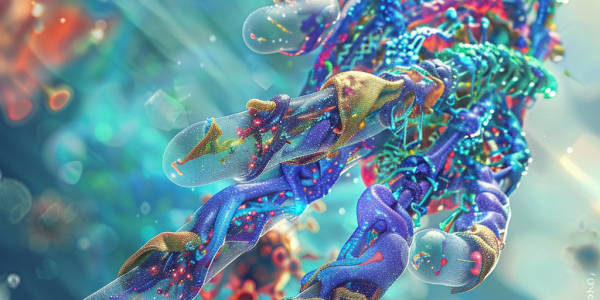
Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed the NanoGripper, a revolutionary DNA origami device designed to target and neutralize virus particles, including those linked to COVID-19. This innovative technology not only showcases the potential of nanotechnology in medicine but also promises rapid virus detection and targeted antiviral treatments, paving the way for advancements in public health and disease prevention.
Research Reveals Protective Role of CO₂ in Cellular Health
Recent research from the University of Utah reveals a surprising role for carbon dioxide (CO₂) in protecting cells from oxidative stress, a key factor in diseases like cancer and neurological disorders. The study shows that bicarbonate from dissolved CO₂ alters the Fenton reaction, reducing harmful DNA damage. This groundbreaking discovery highlights the potential therapeutic benefits of CO₂ in cellular health, challenging its negative perception in climate discussions.
Unlocking the Dark Proteome: New Insights into Human Genetics and Disease
Recent genomic research has unveiled the ‘dark proteome,’ revealing thousands of overlooked genes that encode miniproteins, reshaping our understanding of human biology and disease. This groundbreaking analysis highlights the potential for new medical discoveries, particularly in cancer and various health conditions, as scientists explore these unconventional genetic segments.
New Insights into Cancer Research: The Role of EV-DNA in Antitumor Immunity
In a groundbreaking study published in Nature Cancer, researchers have unveiled the role of extracellular vesicle-derived DNA (EV-DNA) in colorectal cancer metastasis. This research highlights the potential of EV-DNA as a predictive biomarker for postoperative metastasis risk, offering new insights into cancer biology and paving the way for innovative therapeutic strategies.
University of Illinois Develops Revolutionary DNA Nanorobot for Virus Detection and Prevention
Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have unveiled the NanoGripper, a revolutionary nanorobot made from DNA that can detect and neutralize viruses, including COVID-19. This innovative device mimics human hand functionality, utilizing a four-fingered design to grasp viral threats and prevent infections. With potential applications in drug delivery and rapid testing, the NanoGripper represents a significant advancement in nanomedicine, promising improved public health outcomes.
Arc Institute Launches ‘Evo’: A Revolutionary AI Model for Genetic Research
The Arc Institute has launched ‘Evo,’ the first biological foundation model trained on DNA, capable of predicting and designing genetic sequences over one million bases. This groundbreaking tool promises to revolutionize genetic engineering and synthetic biology by enhancing our understanding of DNA and its functions, paving the way for innovations in medicine, agriculture, and environmental sustainability.
DNA Analysis Challenges Long-Held Beliefs About Pompeii Victims
Recent DNA analysis of Pompeii’s iconic plaster casts reveals surprising truths about the identities of victims, challenging long-held beliefs about their relationships and gender roles. This groundbreaking study, published in Current Biology, uncovers that a figure previously thought to be a mother is actually male, prompting a reevaluation of family dynamics in ancient Roman society. The findings highlight the importance of modern scientific techniques in understanding historical events and the diverse backgrounds of Pompeii’s inhabitants.
Study Links Plastic Ingredient BBP to DNA Damage and Reproductive Risks
A new study from Harvard Medical School reveals that benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP), a common plastic ingredient, may cause DNA damage and chromosome errors, raising concerns about reproductive health. This research highlights the toxic effects of BBP, commonly found in consumer goods, and its potential to disrupt genetic integrity, emphasizing the need for regulatory scrutiny and further investigation into the health impacts of plasticizers.
Navigating Privacy Choices and Advances in Genetic Engineering
Explore the critical balance between user privacy and online functionality in the digital age, alongside groundbreaking advancements in genetic engineering. Learn how essential and optional cookies impact your data privacy and discover the potential of engineered cis-regulatory elements for targeted therapies.
Scientists Reconstruct 10,000-Year-Old Genome, Unveiling Ancient African Cultures
Scientists have reconstructed a 10,000-year-old genome from southern Africa, revealing insights into ancient human cultures and their coexistence with pastoralist societies. This landmark study, published in Nature Ecology & Evolution, emphasizes the importance of genetic research in understanding human evolution and migration patterns, particularly through the analysis of genomes from the Oakhurst rock shelter. The findings illuminate the connections between ancient populations and modern inhabitants, enriching our knowledge of southern Africa’s diverse history.