States in the US with Highest Financial Risks from Weather-Related Events
Climate change poses financial risks to states in the US due to environmental events like tornadoes, wildfires, hurricanes, and flooding. SmartAsset study ranks Louisiana highest with $556 in annual damages per person, while Ohio and New York face lowest damages. Understanding these risks is crucial for planning and building resilience.
Corporate America Struggles to Meet Climate Goals Amid Backlash Against ‘Woke Capitalism’
Corporate America is facing challenges in meeting climate goals amidst a growing backlash against ‘woke capitalism.’ Despite some companies struggling to uphold ambitious climate commitments, advocates stress the importance of maintaining momentum in climate action efforts. The debate surrounding the role of corporations in addressing environmental challenges has intensified, reflecting broader societal divisions.
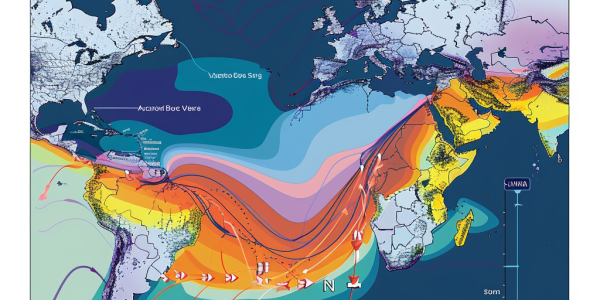
Study Reveals Weakening of Atlantic Abyssal Limb in North Atlantic
A recent study published in Nature Geoscience reveals a weakening of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation abyssal limb in the North Atlantic, impacting heat and carbon redistribution. The study shows a decrease in the transport of Antarctic Bottom Water towards the north, with warming trends contributing to sea-level rise in the region. This weakening is linked to reduced formation rates of Antarctic Bottom Water and abyssal warming in the western Atlantic Ocean.
New Research Examines Impact of Rising CO2 Levels on Global Warming
New research led by the University of Washington examines the relationship between CO2 levels and climate sensitivity, providing insights into future temperature projections. By analyzing the most recent ice age, scientists aim to refine their understanding of how CO2 influences global temperatures. The study narrows the estimate of climate sensitivity, offering a more optimistic outlook for future warming scenarios with higher CO2 concentrations.
Wildfires in Arctic and Boreal Latitudes Impacting Ecosystems
Learn how wildfires are impacting photosynthesis rates in Canada and Alaska, leading to the transformation of boreal forests. Researchers at the University of California, Irvine are studying the effects of wildfires on black spruce forests and the rise of deciduous shrubs and trees in these regions. Find out how these changes could affect carbon dioxide removal and ecosystem functions in the Arctic and boreal latitudes.
Arctic Permafrost Thaw Accelerating Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Arctic permafrost region is now emitting more carbon dioxide and methane than it absorbs, contributing to accelerated global warming. Recent research indicates that the ongoing thaw is likely to persist, worsening the effects of climate change.
Hidden Impacts of Ocean Warming and Acidification Revealed
Groundbreaking meta-analysis reveals the hidden impacts of ocean warming and acidification on marine animals’ biological responses. Study highlights the urgent need for proactive measures to mitigate climate change impacts on marine life and preserve biodiversity.
Antarctic Meteorites Threatened by Climate Warming, Study Finds
A new study published in Nature Climate Change reveals that climate warming is causing many extraterrestrial rocks to be lost from the surface of Antarctica by melting into the ice sheet. The research predicts that approximately 24% of meteorites will be lost by 2050, potentially rising to approximately 76% by 2100 under a high-emissions scenario. The findings raise concerns about the future of Antarctic meteorites and the potential loss of valuable extraterrestrial rocks due to climate warming.
The Black Summer of Our Oceans
Learn about the devastating impact of mass coral bleaching events and marine heatwaves on Australia’s east coast waters, reminiscent of the Black Summer bushfires. Urgent action is needed to address the escalating crisis facing our oceans and the impact of climate change on marine ecosystems.
China’s Rapid Expansion of Electric Power Grid Leads to Surge in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
China’s rapid expansion of its electric power grid has led to a concerning increase in the release of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas, a greenhouse gas 24,300 times more potent than carbon dioxide (CO2) in creating the greenhouse effect. This surge in SF6 emissions poses a threat to global efforts in combating climate change, as it significantly impacts the planet’s radiative budget. The study emphasized the urgency for immediate action to reduce and ultimately eliminate SF6 emissions, stressing the imperative nature of global cooperation in addressing this pressing environmental issue.