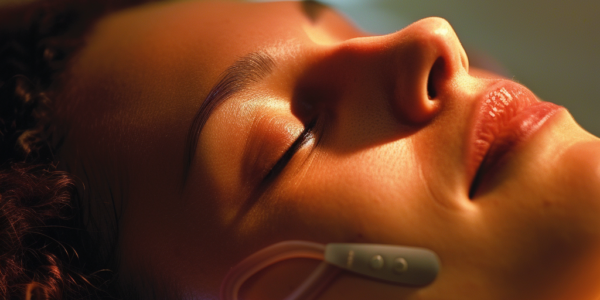
Neuroprosthetic Device Allows Amputees to Feel Natural Sensations from Prosthetic Legs
Neuroprosthetics have advanced to allow amputees to experience natural sensations from artificial body parts. The ETH Zurich Neuroengineering Lab has developed a neuroprosthetic device connected to the sciatic nerve, enabling communication with the brain to relay pressure changes detected on the prosthetic foot. This breakthrough has given test subjects greater confidence and improved their ability to walk on challenging terrains. The team emphasized the significance of evoking natural sensations and highlighted the benefits of using biomimetic stimulation to develop the next generation of neuroprosthetics.
Habits to Prevent Memory Decline in Aging Individuals
Learn about the detrimental habits that can lead to memory decline in aging individuals, and discover the science-backed strategies to prevent memory loss. Find out how multitasking, lack of quality sleep, and engaging in monotonous activities can impact memory, and learn practical tips to enhance memory retention as you age.
The Importance of Quality Sleep in Reducing Stroke Risk
Prioritizing good quality sleep is essential to reduce the risk of stroke, which is on the rise among the younger population. Unhealthy lifestyle habits and risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol are contributing to the increased incidence of stroke. Immediate medical attention is crucial for stroke symptoms, as every minute counts.
Science-Backed Ways to Improve Your Mood
Looking for a pick-me-up? One of the simplest science-backed ways to improve your mood is to get outside in nature. Spending time in nature can help reduce stress, improve mood, and keep you healthy. Additionally, listening to birds has been shown to have a positive effect on mood. Find out more about these science-backed self-care tips and how they can help improve your mental health.
Study Shows Promise of Focused Ultrasound for Pain Management
Discover the groundbreaking study by Wynn Legon on the potential of low-intensity focused ultrasound in pain management. The research demonstrates the noninvasive approach’s ability to target the brain’s pain processing mechanisms, offering new possibilities for pain relief without the risk of addiction. Legon’s study reveals significant reductions in pain perception and physiological responses, signaling a promising future for noninvasive pain management interventions.
Mother Urges Vaccination After Daughter Dies from Measles
Stephanie Peters tragically passed away at 27 from measles, despite initially recovering as a child. Her mother urges parents to vaccinate their children as measles cases surge, emphasizing the severity of the disease and the potential to save lives.
Nerve Stimulation and Rehabilitation Therapy Show Promise in Stroke Recovery
Nerve stimulation combined with intense physical rehabilitation has shown promising results in helping stroke survivors regain movement in their arms and hands, according to a study presented at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2024. The research, conducted by…
The Impact of Alcohol and Drugs on Brain Gene Activity
Alcohol and other drugs have a profound impact on the brain’s reward pathways and can lead to changes in genetic function. This raises the question: how can we combat addiction? Many individuals are naturally inclined to pursue and react to…
The Battle for Your Brain: Defending Cognitive Liberty in the Age of Neurotechnology
Brain-sensing technology is rapidly advancing, raising concerns about the protection of mental privacy. In a recent TED Radio Hour segment, lawyer and AI ethicist Nita Farahany highlighted the potential exploitation of private thoughts and emotions for profit in the absence…
Experiencing racism may physically change your brain
Experiencing racism may physically change your brain Recent research suggests that racism, both in daily life and in healthcare, may contribute to health disparities for Black communities. Scientists are now investigating whether racism can physically alter the brain, potentially explaining…