Study Reveals Superbug Risk in Hospital Sinks
Hospitals are grappling with the presence of drug-resistant bacteria, particularly in sinks, as highlighted by a recent study on superbugs. The study focused on a ‘multispecies outbreak’ of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CPE) in a paediatric ward, underscoring the challenges of combating these drug-resistant superbugs in healthcare settings.
Chinese Scientists Discover Gut Bacteria in Mosquitoes to Combat Dengue and Zika
Chinese scientists have discovered a gut bacteria in mosquitoes that could prevent the transmission of dengue and Zika viruses to humans. Published in Science, the research proposes introducing this bacterium into mosquito populations as a natural strategy to combat these diseases. With millions infected by dengue annually, the study highlights the potential of a nature-based approach to address global health threats posed by mosquito-borne viruses.
Discovery of Antibacterial Umbrella Particles in Streptomyces Bacteria
Recent research in Nature reveals how Streptomyces bacteria produce unique umbrella particles to inhibit the growth of competing bacterial species. These antibacterial complexes contain polymorphic toxin proteins and lectin components, targeting specific Streptomyces species. Unlike broad-acting antibiotics, umbrella particles mediate competition among related species, offering insights into bacterial dynamics in soil ecosystems and potential for novel antimicrobial strategies.
Mouth Bacterium Found in 50% of Colorectal Cancer Tumors
New research reveals a potential link between a bacterium commonly found in the mouth and colorectal cancer, with a specific subtype present in 50% of tumors. This discovery could lead to new screening, prevention, and treatment methods for the disease, offering hope for improved outcomes for patients. The study, published in Nature, highlights the need for innovative approaches to combat colorectal cancer, which has been on the rise in recent years. Understanding the specific subtypes of the bacterium could provide valuable insights into its impact on cancer and potential for targeted treatment.
New Research Project Targets ECF-T Transport Protein to Starve Resistant Bacteria
New research project aims to develop novel active substances to combat antimicrobial resistance. Prof. Anna Hirsch and her team at the Helmholtz Institute for Pharmaceutical Research Saarland have identified a potential target structure, the transport protein ECF-T, which could be disrupted by new drugs to starve resistant bacteria. This approach could lead to the development of effective antibiotics that address previously unused target structures in pathogens.
Study Finds Listeria monocytogenes Bacteria Persist in Ready-to-Eat Food Production Environments
A recent study by scientists from the Quadram Institute and the UK Health Security Agency found that Listeria monocytogenes bacteria can persist in ready-to-eat food production environments despite cleaning. The researchers discovered stable bacterial populations coexisting with L. monocytogenes, suggesting the need for new strategies to alter entire bacterial populations for complete pathogen elimination. The study’s lead scientist, Dr. María Díaz, emphasized the importance of cleaning in reducing bacterial load and mitigating cross-contamination, while also noting significant differences in bacterial populations in areas of the facility kept at different temperatures.
Attack and defence in the microverse
Research team at University of Jena examines the interaction of attack and defence strategies when cholera-causing bacteria are infected with a bacteriophage. Tiny RNA molecules play a decisive role in the complex interaction. The findings have been published in Cell Host & Microbe.
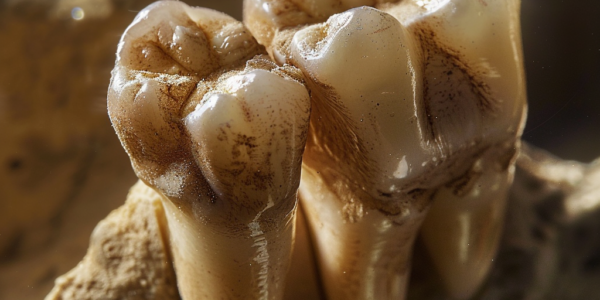
Ancient teeth reveal abundance of bacteria causing tooth decay and gum disease
Discovery of ancient teeth with high levels of cavity-causing bacteria sheds light on the impact of diet changes over the past 4,000 years. The rare find in Ireland’s County Limerick suggests that the prevalence of cavities today may be linked to the consumption of refined sugar and processed foods, which were not part of the ancient human diet.
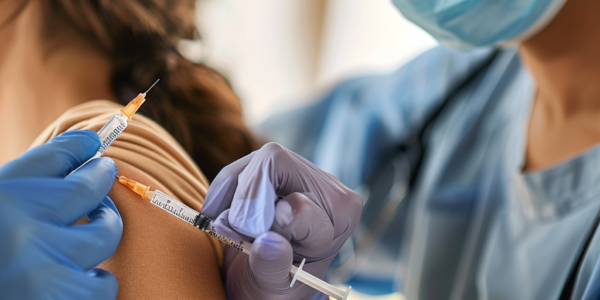
CDC Issues Health Alert for Rare Bacterial Infection
The CDC has issued a health alert regarding a rare bacterial infection, invasive meningococcal disease, which can quickly become fatal. Meningitis, caused by Neisseria meningitidis, can attack the brain, spinal cord, and bloodstream, posing a serious threat to public health. The bacteria can be carried in a person’s nose and throat without causing illness, but individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to infection. The CDC has identified four different groups of meningococcal bacteria circulating in the United States, with the Y bacterial group spreading across the nation. The fatality rate in the cases identified this year stands at about 1 in 6 people, higher than the typical rate observed by the CDC for meningococcal infections. The CDC recommends two vaccines to combat the infection and urges the public to stay informed and take necessary precautions.
Study Links Common Bacteria to Stomach Cancer Development
A new study has found that the typically harmless bacteria, Helicobacter pylori, may play a significant role in the development of stomach cancer. Researchers have identified the mechanism through which this bacteria operates, potentially paving the way for the development of therapeutics to mitigate the risk. The study focused on examining the non-H. pylori gut microbiome in patients with varying stages of gastric cancer, revealing the enrichment of five oral pathogens in the gastric linings of these patients, including Streptococcus anginosus. Through the use of mouse models, researchers observed that colonization with S. anginosus initiated an acute inflammatory response, followed by a chronic phase characterized by intense and persistent gastritis, mirroring the pathway observed in humans before the onset of gastric cancer. Co-infection with S. anginosus and H. pylori resulted in greater gastric inflammation than either pathogen alone, suggesting a potential synergistic effect in promoting gastric cancer.