Astrophysicists Discover Comet-Like Tail on Exoplanet WASP-69 b
Astrophysicists have discovered that the exoplanet WASP-69 b possesses a comet-like tail of gas extending 563,000 kilometers, revealing significant atmospheric loss due to photoevaporation. This hot Jupiter, located 160 light-years away, loses around 200,000 tons of gas per second, primarily hydrogen and helium, shaped by stellar winds. This groundbreaking research enhances our understanding of exoplanetary atmospheres and their dynamics, contributing to the field of astrophysics.
Astronomers Discover Dynamic Earth-Sized Spots at Jupiter’s Poles
Astronomers have discovered massive, Earth-sized dark spots at Jupiter’s poles that appear and disappear unpredictably. Visible only in ultraviolet light, these dynamic ovals challenge previous understandings of Jupiter’s atmospheric stability and magnetic field interactions. This groundbreaking research, published in Nature Astronomy, highlights the complexity of Jupiter’s atmosphere and its unique atmospheric dynamics, offering potential insights into exoplanetary atmospheres.
Decline in Cloud Cover Linked to Record Global Temperatures
Recent research reveals that a significant decline in low-lying cloud cover in 2023 has contributed to record global temperatures, averaging 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. This decrease in cloud cover has reduced Earth’s albedo, leading to increased solar energy absorption. As scientists investigate the complex interplay between cloud dynamics and climate change, understanding these factors is crucial for future climate models and mitigation strategies.
Amazon Rainforest’s Role in Climate Dynamics Unveiled by New Research
Recent research reveals that the Amazon rainforest plays a vital role in climate regulation by emitting isoprene, which is transported to high altitudes by nocturnal thunderstorms, leading to aerosol formation essential for cloud development. This groundbreaking study challenges previous beliefs about isoprene degradation and highlights the rainforest’s significant impact on atmospheric conditions and global climate systems.
Crowdsourced Smartphone Data Revolutionizes Ionospheric Mapping
A groundbreaking study reveals how aggregated data from millions of Android smartphones can enhance ionosphere mapping, improving GPS accuracy and providing critical insights into solar storm impacts. This innovative approach not only boosts scientific understanding but also prioritizes user privacy, making it especially beneficial in regions lacking traditional monitoring stations.
NASA Unveils Insights on Hurricane Helene’s Atmospheric Impact
NASA’s recent findings from Hurricane Helene reveal significant atmospheric phenomena using the Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE). This innovative technology, stationed on the International Space Station, monitors gravity waves in the upper atmosphere, enhancing our understanding of how hurricanes affect satellite operations and communication systems. The data collected during the hurricane’s impact on Florida provides invaluable insights for improving disaster preparedness and response strategies amid increasing storm activity due to climate change.
NASA’s ER-2 Aircraft Advances Earth Science in PACE-PAX Mission
NASA’s ER-2 aircraft has successfully completed over 80 flight hours for the PACE-PAX mission, enhancing our understanding of Earth’s systems. Operating at altitudes up to 65,000 feet, the ER-2 validates satellite data and supports vital research on environmental changes and mineral resources. This collaborative initiative involves multiple organizations, showcasing the importance of interdisciplinary efforts in Earth science and resource management.
Scientists Propose Diamond Dust as Unconventional Solution to Global Warming
Scientists at ETH Zurich propose an innovative geoengineering solution to combat global warming: injecting diamond dust into the atmosphere. This unconventional method could potentially lower global temperatures by 1.6°C, raising discussions on the feasibility and ethical implications of such a massive project. As climate change intensifies, the exploration of alternative aerosol particles like diamonds highlights the urgent need for effective climate solutions.
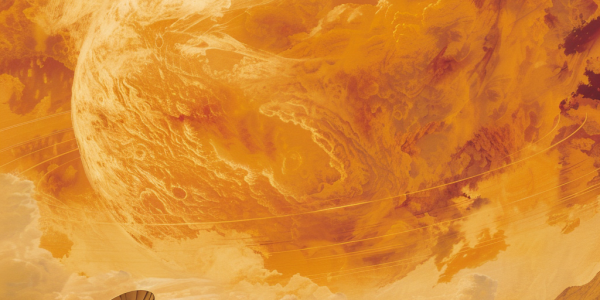
New Evidence of Phosphine on Venus Sparks Life Debate
Scientists have unveiled new evidence of phosphine in Venus’ clouds, reigniting the debate about the potential for life on the planet. Recent findings presented at a Royal Astronomical Society meeting highlight advancements in observational technology, leading to more robust data supporting the initial detection of phosphine. The discovery of ammonia in the atmosphere further complicates the search for extraterrestrial life, prompting renewed interest in Venusian research and future exploration missions.
Study Reveals Impact of Historical Extreme Heat on Ocean Circulation
A recent study by the University of California, Riverside reveals how historical extreme heat events impacted ocean circulation, affecting the global conveyor belt that redistributes heat and stores carbon. The findings, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, highlight the crucial role of oceans in regulating Earth’s climate and sequestering carbon dioxide. Understanding past climate events can provide insights into the future impacts of continued carbon emissions on climate stability.