A recent study by French researchers has found a potential link between certain food additives and an increased risk of cancer. The study, conducted by researchers from Inserm and Inrae and published in the scientific journal PLOS Medicine, is the first of its kind to observe this association.
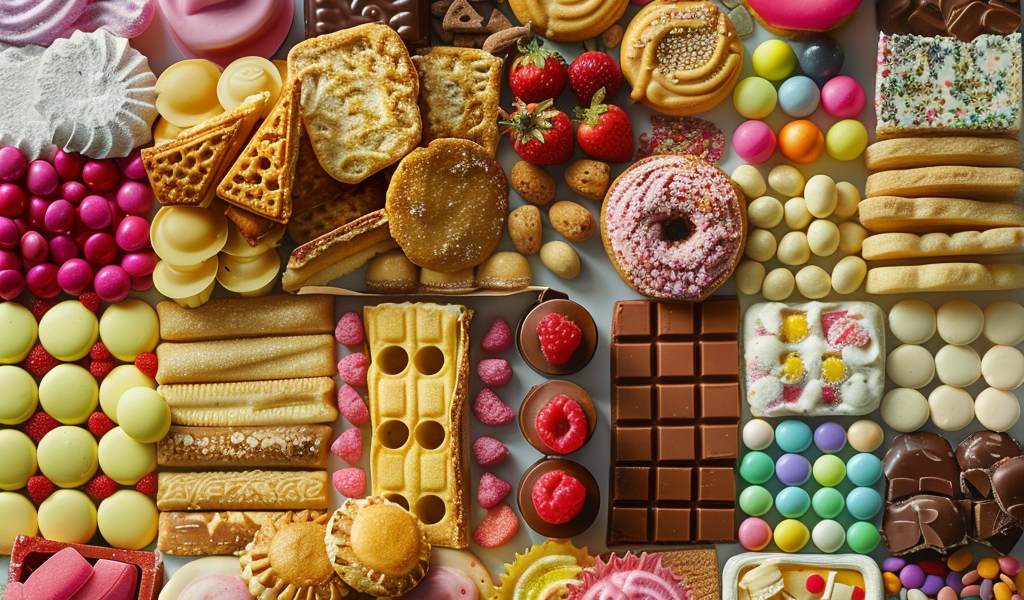
According to the report, consuming foods containing emulsifiers could be linked to a 15% higher risk of cancer, including breast and prostate cancer. Emulsifiers and additives such as E471, E407, and E407a are commonly found in a variety of processed foods, including ready meals, sweets, patisserie, and chocolate bars. These additives are used to enhance texture, flavor, and shelf life of the products.
The study analyzed data from 92,000 participants in France, with 79% of them being women. The participants had reported their food and drink consumption, including brands, on multiple occasions between 2009 and 2021. The researchers then reviewed the health outcomes of the participants over an average of [time period].
The findings of the study raise concerns about the potential health risks associated with the consumption of processed foods containing certain additives. With cancer being a leading cause of death in France, understanding the impact of these additives on health is crucial for public health policy and consumer awareness.
As more research is conducted in this area, it is important for consumers to stay informed about the potential risks associated with the additives in the foods they consume. This study could potentially lead to changes in regulations regarding the use of additives in the food industry, with implications for both manufacturers and consumers.