Optical Coherence Tomography: A Game-Changer in Detecting Ureteral Injuries During Pelvic Surgery
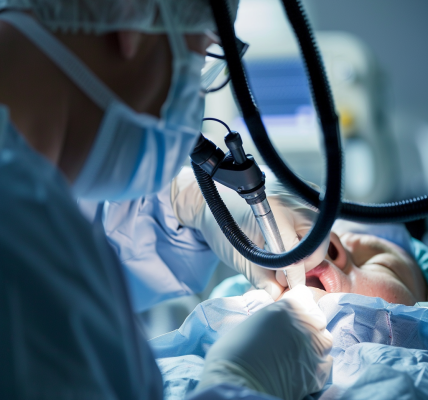
Ureteral injuries during pelvic surgery can be a common complication, with the delicate tubes at risk due to their proximity to other anatomical structures. Detecting these injuries quickly is crucial, as existing methods may not promptly identify subtle thermal damage, which could take time to manifest. A recent study has shown that optical coherence tomography (OCT) endoscopy, a minimally invasive imaging technique, could provide a solution to this challenge.
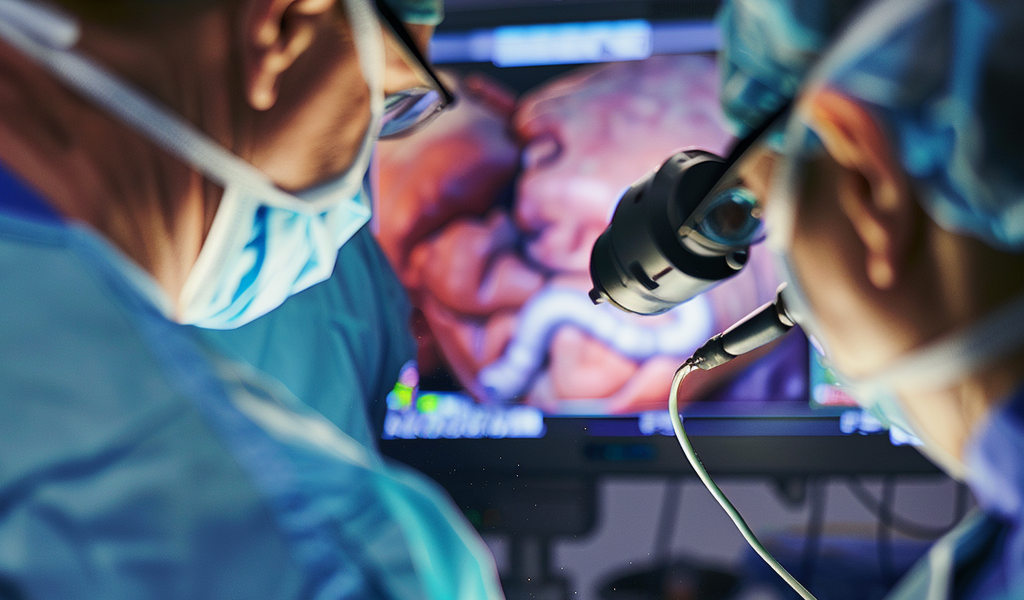
The study highlighted the effectiveness of OCT in visualizing ureteral electrothermal injuries. These injuries, which can occur due to the heat generated during surgery, are often challenging to detect with conventional methods. By utilizing OCT, medical professionals can now have a real-time, detailed view of the ureteral tissue, enabling them to identify injuries promptly and accurately.
Unlike traditional detection methods that may require days or weeks for symptoms to appear, OCT offers immediate visualization of any damage to the ureter. This early detection can lead to timely interventions, potentially preventing further complications and improving patient outcomes.
The use of OCT in detecting ureteral injuries represents a significant advancement in surgical techniques. By providing a non-invasive and precise imaging tool, OCT could revolutionize the way medical professionals approach and manage complications during pelvic surgeries. This technology has the potential to enhance patient safety and surgical outcomes, ultimately benefiting individuals undergoing such procedures.
As medical research continues to explore innovative solutions for enhancing surgical procedures, the integration of advanced imaging technologies like OCT demonstrates the ongoing commitment to improving patient care and treatment outcomes. With further developments and refinements, OCT and similar imaging techniques are poised to play a crucial role in advancing the field of surgical medicine.