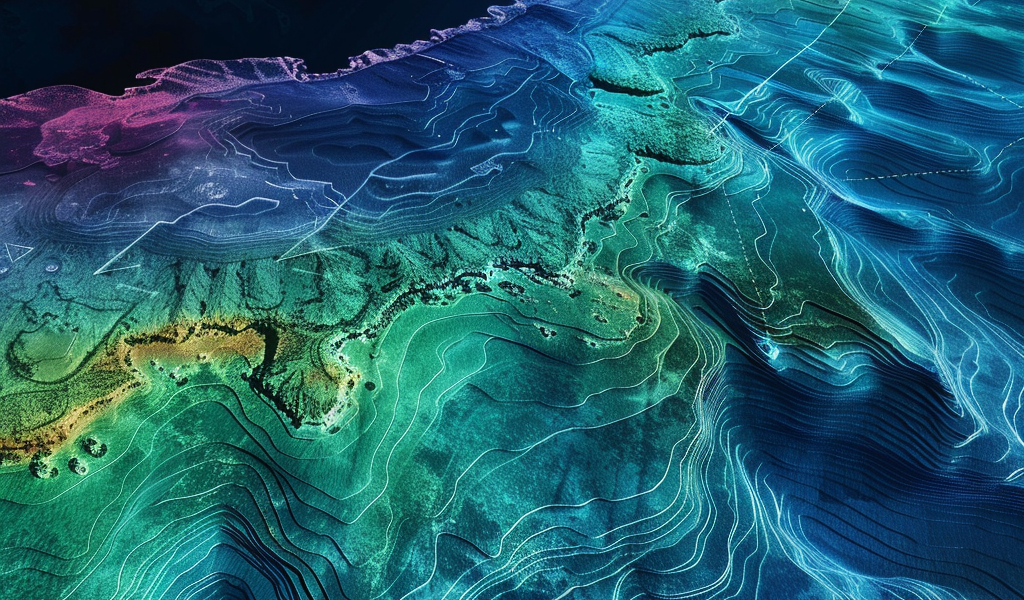
A groundbreaking development in oceanography has emerged from the recent findings of NASA’s Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite, which has produced the most detailed map of the ocean floor to date. Launched in December 2022 in collaboration with France’s Centre National D’Etudes Spatiales, the SWOT satellite has already made a significant impact in its first year of operation, revealing hundreds of previously uncharted underwater hills and volcanoes.
According to a study published in the journal Science on December 12, 2024, the data collected from the SWOT satellite has provided researchers with a clearer understanding of the ocean floor than what was achieved over the past 30 years by older satellites and ships. The satellite boasts a remarkable resolution of 5 miles (8 kilometers) and covers a vast area of the planet every 21 days, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of underwater features.
The innovative technology employed by SWOT measures the height of the ocean surface, which, contrary to popular belief, is not uniform. The gravitational effects of underwater structures, such as hills and volcanoes, create variations in water height, forming what are known as “lumps.” By analyzing these changes in sea surface height, researchers can infer the presence and characteristics of structures located beneath the waves.
In their research, the team focused on three primary types of underwater features: abyssal hills, small seamounts, and continental margins. Abyssal hills, which are parallel ridges rising just hundreds of feet from the ocean floor, are formed through the movements of tectonic plates. The SWOT data allowed the researchers to map these hills in detail and even identify areas where the direction of the ridges shifts, indicating a historical change in the movement of tectonic plates.
Yao Yu, a physical geographer from the Scripps Institution of Oceanography and co-author of the study, expressed surprise at the abundance of abyssal hills discovered in such a short time frame. The findings are expected to advance scientific understanding of tectonic theories and could provide valuable insights into ocean currents, nutrient transport in seawater, and the geological history of our planet’s oceans.
As researchers continue to analyze the data generated by the SWOT satellite, the implications for oceanography and related sciences are vast. The ability to identify and study these previously hidden features of the ocean floor will undoubtedly enhance our understanding of Earth’s geological processes and the dynamics of marine ecosystems.
The SWOT mission represents a significant leap forward in ocean exploration, as it not only maps the ocean floor but also contributes to a broader understanding of the interactions between the ocean and the atmosphere, climate change, and the health of marine environments. The detailed maps produced by the satellite will serve as a crucial resource for scientists, policymakers, and conservationists alike as they work to protect and manage our ocean resources.
With the successful deployment of the SWOT satellite and its impressive capabilities, the future of ocean mapping and research looks promising. As more data becomes available, it will provide an unprecedented opportunity to explore the mysteries of the deep sea and uncover the secrets hidden beneath the surface of our oceans.