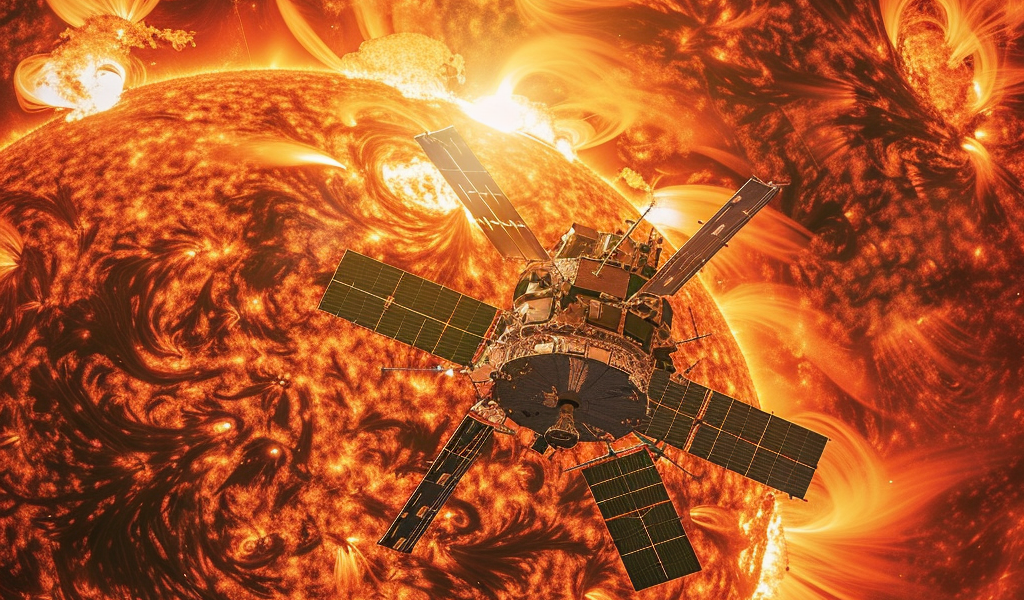
NASA has achieved a groundbreaking milestone in solar exploration by successfully bringing its Parker Solar Probe within an astonishing 4.51 million miles (7.26 million kilometers) of the Sun’s surface. This remarkable event, which occurred on June 30, 2024, marks the spacecraft’s 20th close encounter with our solar system’s star, setting a new record for proximity to the Sun.
The Parker Solar Probe, launched in 2018, was designed with the ambitious goal of unraveling the mysteries surrounding the Sun and its atmosphere. Over the years, it has provided invaluable insights into the solar phenomena that influence space weather and impact Earth. This latest encounter has generated significant excitement within the scientific community, as it promises to deepen our understanding of solar behavior.
One of the most intriguing questions surrounding the Sun is why its outer atmosphere, known as the corona, is significantly hotter than its surface. While the surface temperature hovers around 5,500 degrees Celsius, the corona can reach temperatures of up to one million degrees Celsius. This phenomenon, known as the “coronal heating problem,” has puzzled scientists for over a century.
The Parker Solar Probe’s advanced instruments detected charged particles traveling at remarkable speeds during its recent solar encounter. These observations have led researchers to speculate that magnetic waves within the corona may be responsible for the extreme heat observed in this outer layer. By studying how energy is transferred from the Sun’s surface to its corona, scientists are beginning to piece together the complex mechanisms that govern solar dynamics.
In addition to its findings on coronal heating, the Parker Solar Probe has also uncovered intriguing features in the Sun’s magnetic field known as “switchbacks.” These are sudden, sharp reversals in the magnetic field that can propel energy and particles into the corona. The discovery of switchbacks not only provides a potential explanation for the high temperatures of the corona but also highlights the dynamic forces shaping the Sun’s atmosphere.
The recent solar encounter was part of a broader mission that began on June 25, 2024, and concluded on July 5, 2024. During this time, the Parker Solar Probe harnessed the immense gravitational pull of the Sun to accelerate to incredible speeds, comparable to traveling from New York to London in under 30 seconds. Such rapid movement allows for detailed observations of solar phenomena that are otherwise difficult to study.
The implications of these discoveries are profound. Understanding the mechanisms behind solar heating and the behavior of the Sun’s magnetic field can have far-reaching effects on our ability to predict solar events and their potential impact on Earth. Solar storms, which can disrupt communication systems and power grids, are influenced by the Sun’s activity. Insights gained from the Parker Solar Probe’s mission could enhance our preparedness for such events.
As the Parker Solar Probe continues its journey, scientists eagerly anticipate further revelations about the Sun. Each close encounter brings with it the potential for new discoveries that could reshape our understanding of solar physics and its implications for life on Earth.
This remarkable mission exemplifies NASA’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of space exploration and scientific discovery. The Parker Solar Probe not only represents a technological marvel but also serves as a testament to human curiosity and the quest for knowledge about the universe we inhabit.
As we look to the future, the Parker Solar Probe’s findings will undoubtedly play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the Sun and its influence on our solar system. The ongoing research and analysis of the data collected during these encounters will continue to illuminate the mysteries of our nearest star, paving the way for future exploration and discovery.