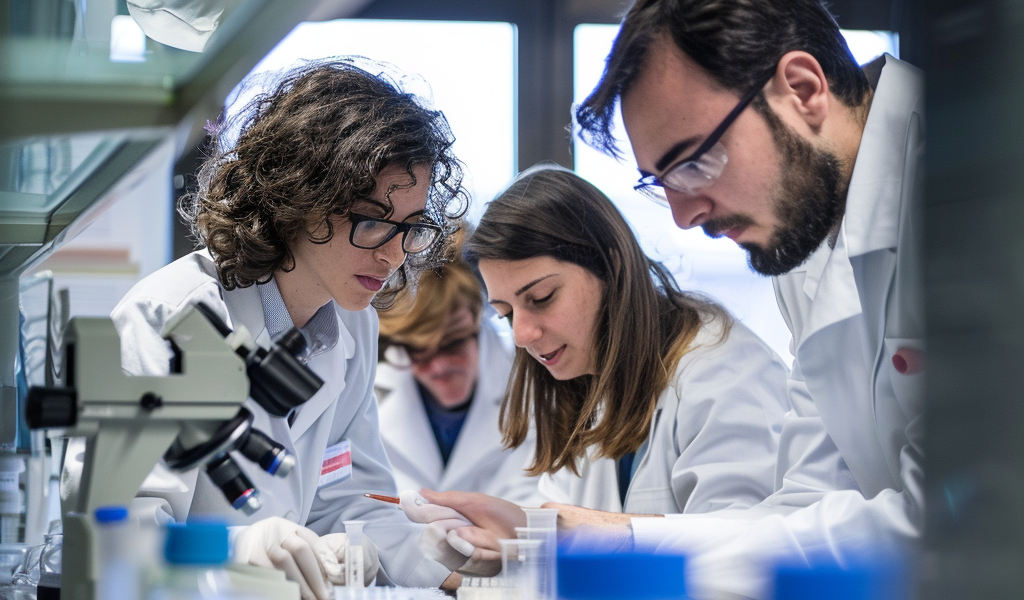
Researchers at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT) in Genoa and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble have made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of gene expression modulation using small molecules. This discovery has the potential to lead to the development of new drugs targeting genetic mutations and alterations that impact gene expression, with implications for treating tumors and genetic diseases.
The study, published in Nature Communications, was led by Marco De Vivo from IIT and Marco Marcia from EMBL. By combining expertise in biochemistry, biophysics, and structural biology, the research team was able to gain insights into how small molecules can influence the splicing process—a critical step in gene expression.
Splicing is a complex process where specific sequences of RNA are ‘cut and pasted’ to create functional RNA versions that play essential roles in the cell. Understanding and modulating this process can have significant implications for various cellular functions, including protein production and cellular regulation.
The research team utilized advanced molecular simulation techniques to study the interactions of molecules involved in splicing. By integrating experimental data from X-ray photographs of the process obtained using the MASSIF-1 beamline, the researchers were able to gain a detailed understanding of the molecular mechanisms at play.
According to the researchers, the study of RNA splicing is challenging due to the intricate chemical reactions and molecular components involved. However, their findings have provided valuable insights into how to intervene and modulate the splicing process effectively.
This collaborative effort between IIT and EMBL highlights the importance of interdisciplinary research in advancing our understanding of complex biological processes. The identification of new molecules that can modulate gene expression opens up exciting possibilities for the development of targeted therapies for various genetic conditions.