Groundbreaking Discoveries in Non-Invasive Neural Interfacing: Unraveling the Effects of Muscle Fatigue on Neural Activity
Groundbreaking Discoveries in Non-Invasive Neural Interfacing: Unraveling the Effects of Muscle Fatigue on Neural Activity
In a pioneering study published on February 11, 2024, researchers delved into the complex interplay between muscle fatigue and neural activity. Focusing on the persistent inward calcium and sodium currents (PICs) responsible for motor neuron firing and muscular force, the team discovered intriguing alterations following fatiguing exercise. These findings offer new insights into the potential implications of fatigue-induced PIC changes on motoneuron output, paving the way for more advanced non-invasive neural interfacing technologies.
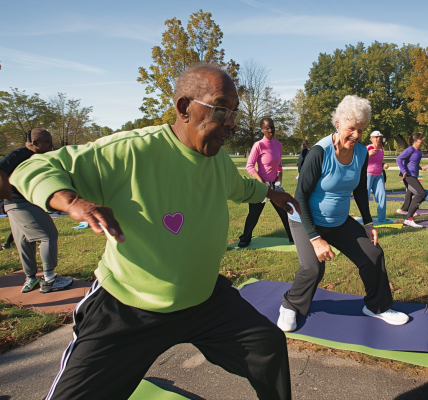
The research investigated the effects of fatiguing exercise on PICs, which are essential for initiating and maintaining motoneuron firing and muscular force. By applying tendon vibration and neuromuscular electrical stimulation (VibStim) before and after fatiguing exercise, the team successfully evoked self-sustained muscle activity, a direct result of PIC activation. The sustained torque and soleus electromyogram amplitudes (EMG) measured 3 seconds after VibStim revealed a significant reduction, indicating the impact of fatigue on these crucial currents.
This new understanding of the relationship between muscle fatigue and neural activity could revolutionize the field of non-invasive neural interfacing. As EMG processing becomes more sophisticated, the ability to accurately interpret and respond to the body’s electrical signals could lead to breakthroughs in prosthetics, rehabilitation, and even communication for those with severe neuromuscular disorders.
In a parallel development, scientists have created a flexible sensor designed specifically for non-invasive neural interfacing through EMG processing. This innovative device, composed of electrospun nanofibers infused with highly conductive nanoparticles and coated with polyaniline, boasts an impressive piezoelectric effect. This attribute eliminates the need for an external battery, as the sensor can generate its own charge in response to electrical signals from the human body.