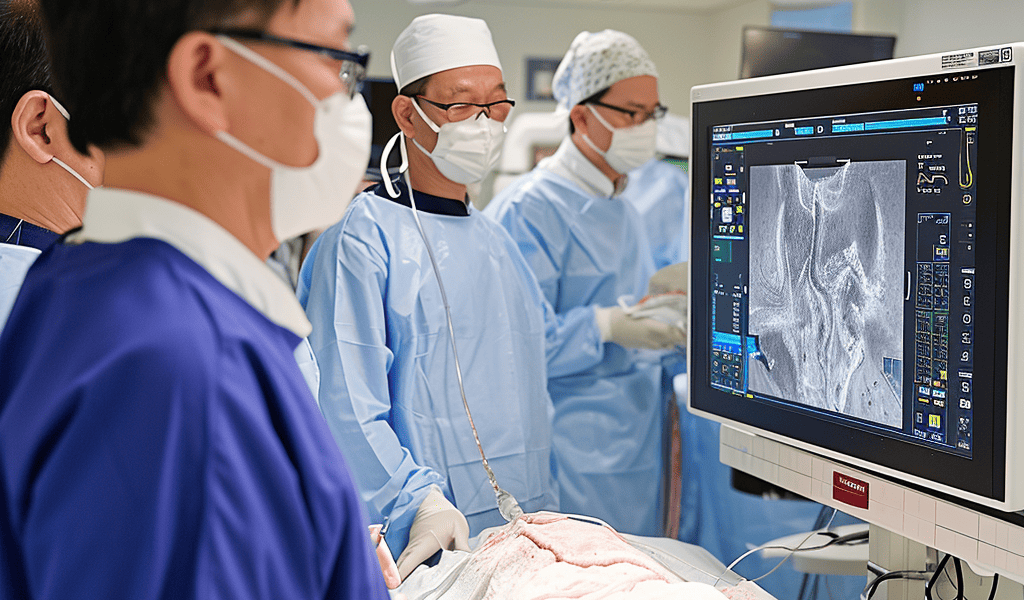
On 9th January 2024, a groundbreaking development in the field of medical imaging was published in the latest issue of Nature Publishing Group journal: Scientific Reports. The research conducted by Prof. Jin Won Kim and Dong Oh Kang’s team from Korea University Guro Hospital, along with Prof. Hongki Yoo and Hyeong Soo Nam from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, introduced a pioneering approach in the application of non-contrast optical coherence tomography (OCT) for patients with coronary artery disease.
Coronary artery disease is a prevalent and serious condition, and the ability to visualize coronary microstructures and assess procedural optimization following stent implantation is crucial for effective treatment. While intracoronary OCT has been widely available in contemporary catheterization laboratories, its requirement for a flushing solution for image acquisition has been a limitation. The commonly used flushing media, radiological iodine contrast, poses risks for worsened renal function with increased usage.
Prof. Kim and Prof. Kang’s research team addressed this challenge by utilizing plasma expander fluid (10% hydroxyethyl starch) as an alternative to iodine contrast agents. Their study validated the clinical feasibility and in-vivo biosafety of non-contrast OCT imaging for patients undergoing coronary stent implantation. The innovative non-contrast OCT imaging using hydroxyethyl starch solution demonstrated intracoronary images of equivalent quality to those obtained using conventional iodine contrast agents.
Furthermore, the implementation of an automated customized pixel-based image analysis algorithm showed comparable results between the paired images obtained using iodine contrast and non-contrast media. Importantly, the non-contrast OCT imaging showed no additional complications or side effects, ensuring the safety of the image acquisition process for all participants included in the study.
Prof. Dong Oh Kang and Hyeong Soo Nam, the first authors of the research paper, highlighted the significance of their findings, stating, ‘We introduced an innovative imaging strategy that can replace conventional iodine contrast agents for obtaining intracoronary OCT images. Our study stands as the world’s first demonstration of the clinical feasibility and safety of non-contrast optical coherence tomography for patients with coronary artery disease.’