Dengue Fever Cases Surge Across the Americas: Key Facts and Insights
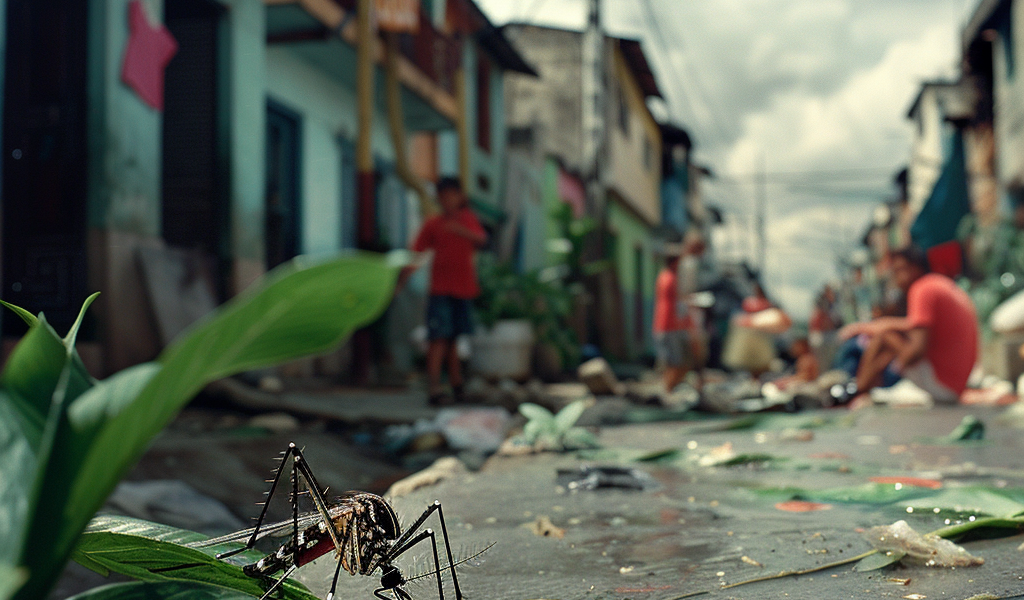
Dengue fever, a mosquito-borne viral infection, is experiencing a significant surge in the Americas, with reported cases increasing by an astonishing 232% compared to the previous year. This alarming rise has raised concerns among health officials and the general public alike, prompting a closer look at the disease, its symptoms, and preventive measures.
Understanding Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is caused by the dengue virus, which is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes, primarily Aedes aegypti. Symptoms typically manifest within four to ten days after being bitten and can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
- High fever
- Severe headaches
- Pain behind the eyes
- Joint and muscle pain
- Rash
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
In some cases, dengue can progress to severe dengue, which can lead to serious complications and even death. Severe dengue is characterized by severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, rapid breathing, bleeding gums, fatigue, and restlessness.
Current Situation in the Americas
Health authorities are sounding the alarm as nearly 10.4 million cases of dengue fever have been reported across the Americas this year alone. The drastic increase in cases is attributed to several factors, including climate change, urbanization, and increased mosquito breeding grounds. Warmer temperatures and heavy rainfall create ideal conditions for mosquitoes to thrive, leading to a higher risk of transmission.
Countries such as Brazil, Mexico, and Colombia are among the most affected, with health ministries implementing various measures to combat the outbreak. These measures include public awareness campaigns, mosquito control programs, and increased funding for healthcare resources.
Preventive Measures
Preventing dengue fever largely relies on reducing mosquito populations and minimizing exposure to bites. Here are some effective strategies individuals can adopt:
- Eliminate Standing Water: Mosquitoes breed in stagnant water. Regularly check and empty containers that collect water, such as flower pots, buckets, and birdbaths.
- Use Insect Repellent: Apply insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus on exposed skin, especially during peak mosquito activity times (early morning and late afternoon).
- Wear Protective Clothing: When outdoors, wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants to minimize skin exposure to mosquitoes.
- Install Screens: Ensure that windows and doors are fitted with screens to keep mosquitoes out of living spaces.
- Community Engagement: Participate in community clean-up efforts to remove potential mosquito breeding sites.
Health Officials’ Recommendations
Health officials are urging individuals to remain vigilant and proactive in preventing dengue fever. They recommend seeking medical attention if symptoms appear, especially in areas experiencing high transmission rates. Early diagnosis and proper medical care are crucial in managing the disease and reducing the risk of severe complications.
Moreover, health departments are emphasizing the importance of vaccination. While there is no specific treatment for dengue, a vaccine called Dengvaxia has been approved in some countries for individuals aged 9 to 45 who have had at least one previous dengue infection. Vaccination can help reduce the severity of the disease in those who contract it again.
Conclusion
The rise in dengue fever cases in the Americas serves as a reminder of the ongoing challenges posed by mosquito-borne diseases. As health officials work to contain the outbreak, public awareness and individual preventive measures will play a crucial role in combating this health threat.