NASA Launches PACE Satellite to Study Oceans and Atmosphere
NASA has launched the PACE satellite to study the world’s oceans and atmosphere. The satellite, which stands for Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, Ocean Ecosystem, will spend at least three years collecting data from an orbit 676 kilometers above the Earth’s surface. Scientists expect to start receiving data within one or two months, providing an unprecedented view of our home planet.
New Genetic Analysis Reveals Insights into Beethoven’s Battle with Hearing Loss
Discover the latest revelation about composer Ludwig van Beethoven’s health, shedding light on his progressive hearing loss. Genetic analysis on authenticated hair samples has provided unprecedented insights into Beethoven’s enduring struggle with hearing loss, offering a new perspective on his medical history and musical career.
Garena Free Fire Max Releases New Redeem Codes for February 20, 2024
Garena Free Fire Max has released new redeem codes for February 20, 2024, offering free in-game goodies such as skins and weapons. The limited-time codes are creating anticipation and engaging players, adding to the game’s appeal in India. The 12-digit alphanumeric codes can be used to claim exclusive in-game items and enhance the gaming experience.
Study Finds Link Between Finger Length Ratio and Oxygen Metabolism Efficiency in Athletes
A recent study from Swansea University reveals the correlation between finger length ratio and oxygen metabolism efficiency in athletes. The research, published in the American Journal of Human Biology, highlights the impact of the 2D:4D ratio on oxygen metabolism, with implications for disease severity and athletic performance.
White and Black Turmeric: Potential Benefits in Fighting Chronic Diseases
Discover the potential health benefits of white and black turmeric in combating chronic diseases. These lesser-known varieties offer unique compounds that have strong anti-inflammatory properties and can help combat oxidative stress, reducing the risk of various chronic inflammatory conditions and diseases.
Genomic Data in the All of Us Research Program
The All of Us Research Program is making significant strides in mapping the genetic basis of human disease, with a focus on diversity and inclusion. The latest release includes 245,388 clinical-grade genome sequences, with a high percentage of participants from historically under-represented communities and racial and ethnic minorities. The comprehensive dataset has identified over 1 billion genetic variants, with coding consequences for over 3.9 million, and is publicly available for researchers to access. This diverse dataset is expected to advance the promise of genomic medicine for all.
The Interconnected Nature of Spring Allergies
Learn how spring allergies can affect multiple systems within the body, from nasal allergies and asthma to eczema and eye allergies. Understanding the interconnected nature of allergic responses is crucial for effectively managing and improving quality of life for those affected.
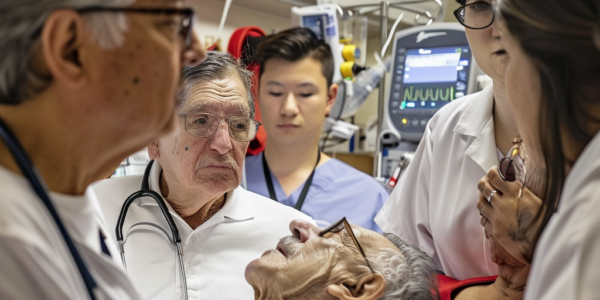
Higher Sedation Rates for Hispanic Patients on Ventilators May Impact Survival
Hispanic Americans on ventilators have a higher risk of death than white peers, possibly due to heavy sedation. Research from NYU and University of Michigan found that Hispanic patients in respiratory failure receive heavy sedation at a rate five times that of white patients, potentially lowering their odds for survival. The study suggests that language barriers, cultural differences, and hospital quality may be contributing factors.
Prevalence of Nonprescribed Weight-Loss Product Consumption Among Adolescents: 5 Key Takeaways
A recent systematic review and meta-analysis published in JAMA uncovered 5 key takeaways about the prevalence of nonprescribed weight-loss product consumption among adolescents, shedding light on this concerning trend.
UC Davis Researchers Identify Gut Microbiome Changes Linked to Sorbitol Intolerance
UC Davis researchers have found that changes in the gut microbiome can lead to an inability to digest sorbitol, a sugar alcohol found in sugar-free products. A study with mice revealed that taking antibiotics and a high-fat diet reduced the number of Clostridia gut microbes responsible for breaking down sorbitol. The research suggests that an impairment in the microbial ability to break down sorbitol causes sorbitol intolerance, and efforts to restore the gut bacteria’s ability to break down sorbitol were successful in protecting the mice from sorbitol-induced diarrhea.