Citizen Scientists Join Researchers in Groundbreaking Global DNA Collection Project
The LeDNA project is set to create the largest collection of environmental DNA (eDNA) ever gathered from aquatic environments in a single day, providing a comprehensive snapshot of global biodiversity. Citizen scientists are teaming up with researchers to collect DNA samples from hundreds of lakes across the globe, with over 500 individuals from 101 countries participating in the initiative. Environmental DNA has been instrumental in detecting endangered species and is considered a valuable asset for biodiversity monitoring, although researchers acknowledge its limitations.
Study Challenges Understanding of Soil Microbiome Diversity and Carbon Cycle
A recent study from the University of Vienna challenges existing understanding of soil microbiomes’ impact on the global carbon cycle. The research found that warmer soils increase microbiome diversity, affecting carbon release. This suggests that carbon release is not solely due to accelerated microbe growth, but also from previously dormant bacteria. The study’s lead author emphasized the complexity of soil microbiome dynamics in response to temperature changes.
Clarkia Middle Miocene Fossil Site: A Key to Understanding Life Beyond Earth
Researchers have been studying the Clarkia Middle Miocene Fossil Site in Idaho, which has provided valuable insights into ancient environmental conditions and the potential for life on Mars. The well-preserved fossils dating back over 11 million years have become a focal point for studying the potential for life on other planets, particularly Mars. The site’s sediments have been used to study biomarkers, offering valuable information about Earth’s history and ancient environmental conditions on Mars. The research conducted at the site represents a significant step forward in our understanding of potential life beyond Earth, paving the way for new insights into the search for extraterrestrial life.
Groundbreaking Discovery: Water Molecules Detected on Surface of Two Asteroids for First Time Ever
Scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery by detecting water molecules on the surface of two asteroids for the first time ever. The data was collected using NASA’s now-retired SOFIA airborne observatory, shedding new light on the distribution of water in our solar system. This groundbreaking discovery opens up new avenues for understanding the composition and distribution of water in our solar system, offering valuable insights into the origins of water on Earth and other celestial bodies.
Research Highlights Potential Impact of Individual Weather Events on Sea Level Rise
Recent research has highlighted the potential impact of individual weather events on the world’s largest ice sheets and, consequently, on sea level rise. A heat wave in Greenland and a storm in Antarctica have raised concerns about the long-term effects of such events, especially in the context of a warming climate. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), global sea levels are projected to rise by 28 cm to 100 cm by 2100. This wide range of estimates underscores the uncertainty surrounding future sea level rise and its potential implications for millions of people worldwide.
The Vanishing Y Chromosome and the Future of Men
The Y chromosome is degenerating and may disappear in a few million years, leading to our extinction unless we evolve a new sex gene. A recent paper in Proceedings of the National Academy of Science shows how the spiny rat has evolved a new male-determining gene. The article also explains how the Y chromosome determines human sex and the disappearing Y chromosome in mammals.
Surge in Electric Bike Injuries and Hospitalizations in Recent Years
Research shows a significant increase in electric bicycle (e-bicycle) injuries and hospitalizations in the United States since 2017, with a particular surge in head injuries. The study found a 30-fold rise in e-bicycle injuries and a 43-fold increase in hospitalizations over the five-year period, with a significant increase in head trauma. The authors emphasize the need for further examination of these trends, as traumatic brain injuries are more severe in e-bicyclists than in traditional bicyclists.
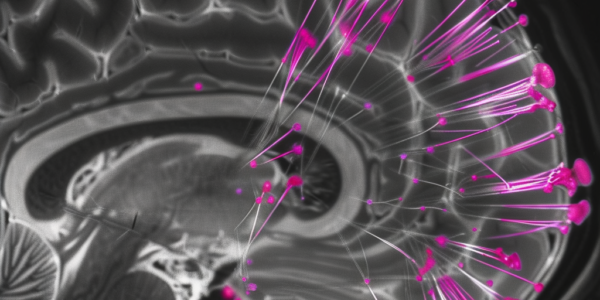
Stanford Medicine Study Reveals Groundbreaking Findings on Male and Female Brain Organization Patterns
Stanford Medicine’s recent study unveils groundbreaking findings on distinctions between male and female brain organization patterns. The research introduces a powerful new artificial intelligence model capable of distinguishing between male and female brains with over 90% accuracy. The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, addresses the controversy surrounding reliable sex differences in the human brain and emphasizes the significance of sex in human brain development, aging, and the manifestation of psychiatric and neurological disorders.
Measles Outbreak at Manatee Bay Elementary School in Florida
Parents of students at Manatee Bay Elementary School in Weston, Florida, have the option to keep their children at home due to confirmed cases of measles. Broward Superintendent Dr. Peter Licata announced that Thursday is the deadline for parents to decide whether their vaccinated or unvaccinated children will stay home for the next 21 days and engage in online continuing education with individualized assignments, emphasizing that it will not be a virtual experience. The school reported 6 confirmed cases of measles and a total of 33 unvaccinated students. As district officials await further directives, they continue to focus on cleaning and sanitizing the school, with no indication of broader county-wide issues at present.
Norovirus Cases on the Rise in the US, Especially in the Northeast
Cases of norovirus are on the rise in the US, particularly in the Northeast, with over 12% of tests coming back positive for the highly contagious virus. Despite the increase, current levels are still below those observed at the same time last season. Norovirus outbreaks are most prevalent in the late fall, winter, and early spring, and the virus causes millions of illnesses annually. The CDC recommends preventive measures such as frequent handwashing and proper food preparation to avoid illness.