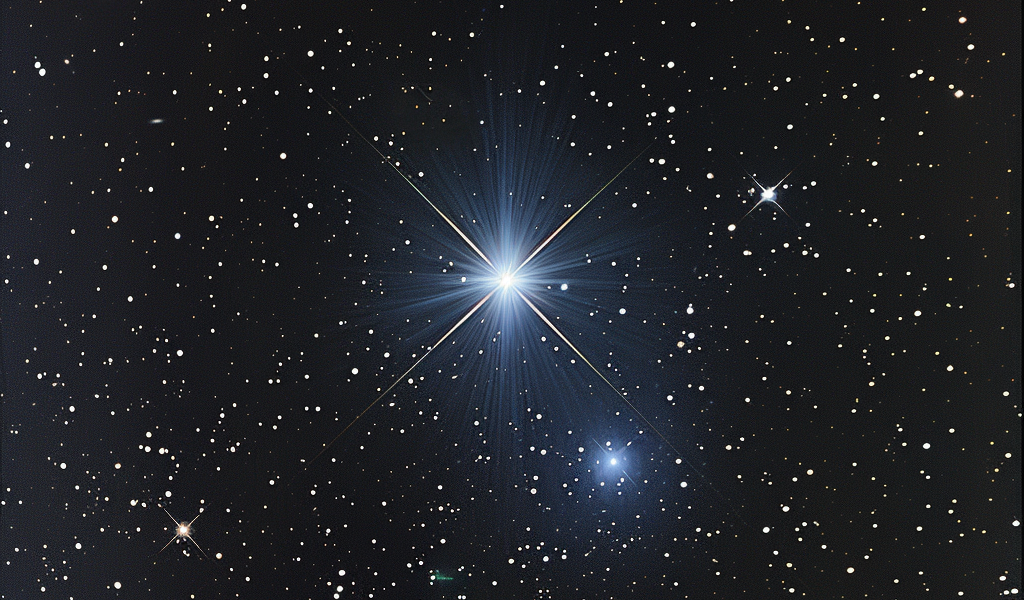
Astronomy enthusiasts are eagerly anticipating the potential brightening of the star system T Coronae Borealis, also known as T CrB or the ‘Blaze Star’, located 3,000 lightyears away. This celestial event, known as a ‘nova’, could see the star’s brightness increase significantly, making it visible to the naked eye for a brief period.
Historically, T Coronae Borealis last brightened in 1946, and astronomers are now speculating that it may undergo a similar brightening phase between now and September 2024. The term ‘nova’ originates from Latin, meaning ‘new star’, and signifies the sudden increase in brightness of a previously dim celestial object, transforming it into a prominent feature in the night sky.
Under normal circumstances, T Coronae Borealis shines at a magnitude of +10, a measure used by astronomers to gauge the relative brightness of celestial bodies as observed from Earth. During the anticipated nova event, the star is predicted to reach a magnitude of +2, comparable in brightness to the North Star, Polaris. This enhanced brightness could make it visible to the naked eye for several days and potentially observable through binoculars for over a week.
Following the brightening of T Coronae Borealis, astronomers and stargazers are advised to monitor astronomy resources and stay updated on developments regarding this rare astronomical occurrence. The nova event is expected to manifest in the constellation Corona Borealis, which may pose a challenge for some observers due to its relatively inconspicuous nature. To locate the constellation, one can refer to nearby star patterns such as Boötes and Hercules, with Boötes being identifiable by tracing the ‘handle’ of the Plough star pattern.
For those interested in capturing this unique event through astrophotography, preparations can begin by familiarizing oneself with the position of Corona Borealis in the night sky. By staying informed and actively observing the skies, enthusiasts may have the opportunity to witness and document the brief yet captivating transformation of T Coronae Borealis into a ‘new star’.