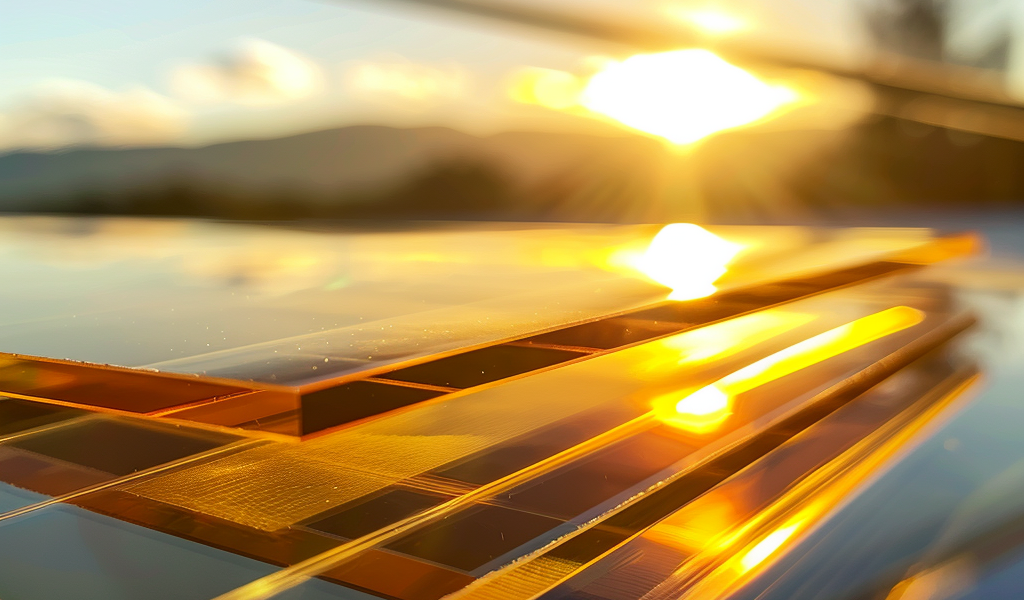
Scientists in South Korea have made a significant breakthrough in the development of semi-transparent perovskite solar cells, bringing us one step closer to windows that can generate energy. The latest tests have shown that these solar cells achieved an efficiency of over 21 percent, which is a record for this type of technology. Additionally, the cells maintained over 99 percent of their initial efficiency for up to 240 hours of operation.
Developed by the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER), the new solar cell technology replaces the metal electrodes of typical solar cells with transparent electrodes that allow light to pass through. However, the process faced challenges as initial tests with the semi-transparent materials resulted in reduced charge transporting properties and stability. To overcome this, the researchers closely analyzed the material using electro-optical analysis and atomic-level computational science.
It was discovered that lithium ions were causing the problem by diffusing into the metal oxide layer, degrading its useful qualities. To address this issue, the researchers converted the lithium ions into stable lithium oxide, significantly improving the stability of the solar cells.
Dr. Ahn SeJin, leader of the researcher at the KIER’s Photovoltaics Research Department, stated, “This study represents a significant advance in the field by examining the degradation process occurring at the interface of organic compound and metal oxide buffer layer, which is unique to semi-transparent perovskite solar cells. Our solution is readily implementable, demonstrating great potential for the future use of the technologies we have developed.”
This development holds promise for the future use of solar energy as a major player in the transition away from fossil fuels. With ongoing advancements in solar cell technology, the potential for windows to serve as solar energy collectors is becoming increasingly feasible, offering a glimpse into a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.