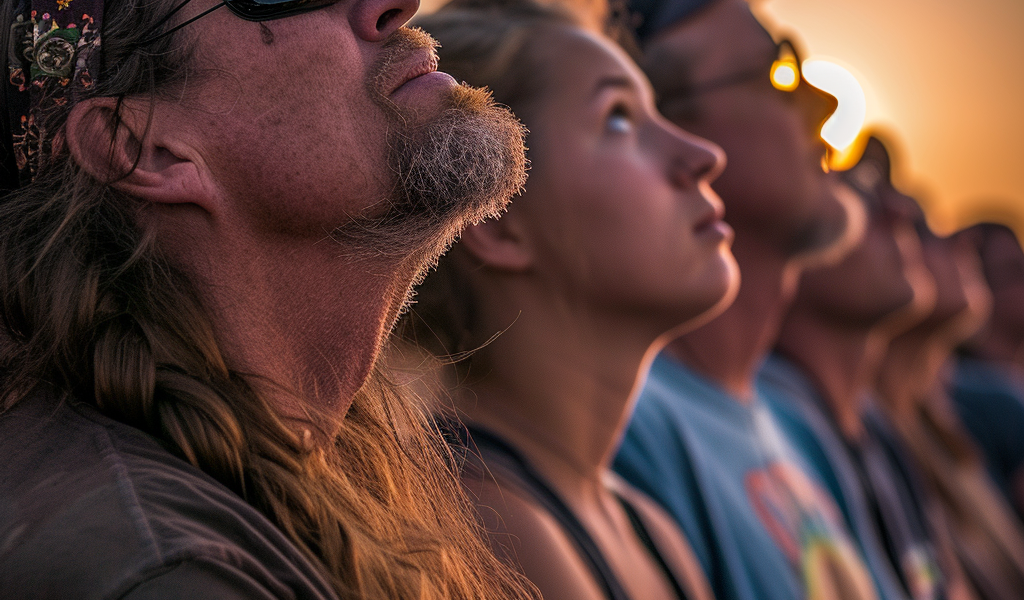
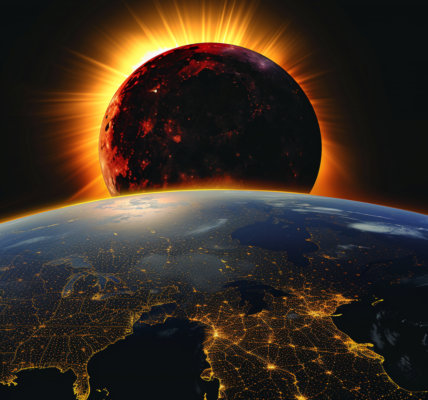
On April 8, 2024, North American sky-gazers will experience one of the decade’s most buzzed-about interstellar events: a total solar eclipse. During this event, the moon will slide between Earth and the sun, turning day into eerie dusk along a roughly 100-mile-wide ribbon of North America, known as the path of totality.
Casting a shadow from Mazatlán, Mexico, to Canada’s Maritime Provinces, the eclipse is predicted to be among the most watched of all time. In the United States alone, over 31 million people reside along the path of totality, which spans 13 states from Texas to Maine; as many as three million may travel to watch it. And for the first time on a large scale, people with visual impairments will be able to experience it, too—by listening.
A team at the Harvard University Astronomy Lab has developed LightSound, a smartphone-sized device that translates ambient brightness into sound. The piping of a flute represents bright daylight, while a clarinet indicates the eclipse’s gradual dimming effect. Soft clicks mark the fleeting few minutes of totality, when the moon completely blocks all but the sun’s fiery outer atmosphere, known as the corona.
These quiet sounds are designed to complement, not detract from, the multisensory event. “You want to experience your surroundings,” says Harvard astronomy lab manager and eclipse chaser Allyson Bieryla. During totality, observers can feel the temperature drop; some may hear unexpected creatures, such as owls or crickets—not to mention emotional crowd reactions. “Some people start cheering, others are crying,” says Bieryla.
LightSound began to be developed before the 2017 total solar eclipse. “It really struck me that we weren’t including everyone in [eclipse] events,” says Bieryla. She teamed up with blind astronomer Wanda Diaz Merced, who pioneered the use of sonification—turning data into sound—for analyzing data sets such as gamma ray bursts. The team started with three devices for the 2017 eclipse, then brought on student Sóley Hyman, who’s also a musician, to redesign the device and its sounds ahead of this year’s show.
The Harvard University Astronomy Lab plans to build and disseminate more than 700 LightSound units.