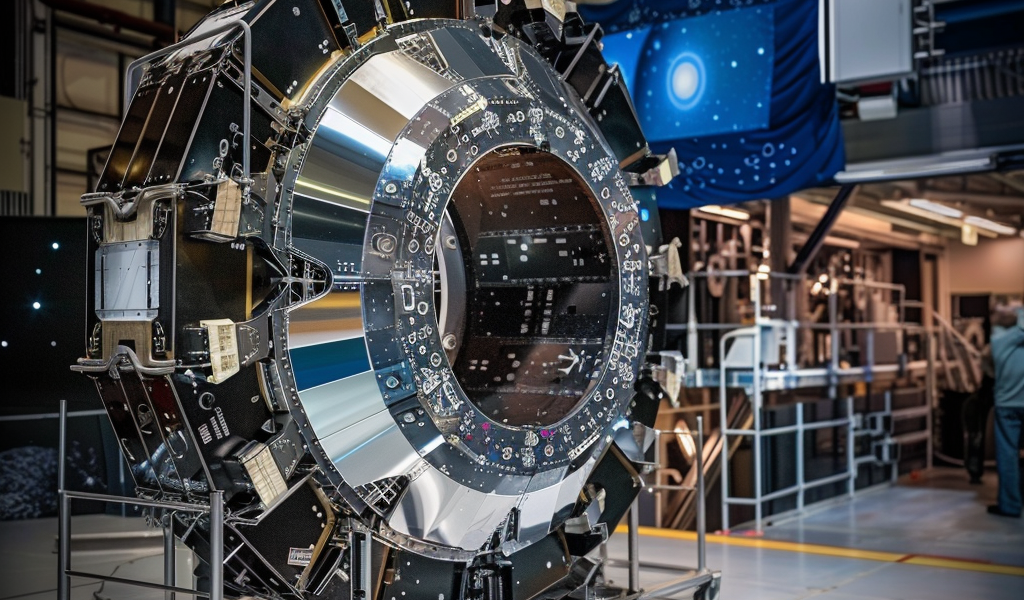
NASA has achieved a significant milestone in its ambitious space exploration efforts with the successful integration of the Roman Space Telescope payload. The integration process, which was completed recently, marks a crucial step towards the telescope’s mission to uncover the mysteries of the universe.
The Roman Space Telescope, named after the renowned astronomer Nancy Grace Roman, is designed to enhance our understanding of dark energy, dark matter, and the existence of exoplanets beyond our solar system. The payload integration involved the assembly of the telescope and two advanced instruments onto an instrument carrier, a critical component of the telescope’s functionality.
The integration process began with the Coronagraph Instrument, which employs innovative technology to capture images of distant exoplanets. By utilizing masks and active mirrors, engineers were able to effectively mitigate the glare produced by the stars that surround these planets, allowing for clearer imaging and data collection.
Following the successful integration of the Coronagraph Instrument, the Optical Telescope Assembly was added. This assembly is pivotal to the telescope’s operation, featuring a primary mirror along with nine additional mirrors, supporting structures, and advanced electronics. The Optical Telescope Assembly is engineered to focus cosmic light and transmit it to the Roman’s instruments, enabling precise measurements essential for scientific research.
In addition to these components, the Wide Field Instrument, a state-of-the-art 300-megapixel infrared camera, was integrated into the payload. This powerful camera will allow scientists to observe a vast array of celestial phenomena, including exoplanets, distant stars, galaxies, black holes, and the elusive dark matter and dark energy that permeate the universe.
As the integration phase comes to a close, the focus will now shift to attaching the instrument carrier to the Roman spacecraft. This crucial task will be carried out by the skilled team at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, located in Greenbelt, Maryland. Additionally, the deployment of the aperture cover, designed to shield the telescope from unwanted light interference, will also be integrated into the telescope’s protective exoskeleton.
The Roman Space Telescope is on track for completion by fall 2026, with plans for its launch into orbit scheduled for May 2027. This timeline reflects NASA’s commitment to advancing our understanding of the cosmos and addressing fundamental questions about the nature of our universe.
The Roman mission is expected to significantly enhance our knowledge of various astronomical phenomena and contribute to ongoing research in the fields of astrophysics and cosmology. With cutting-edge technology and innovative design, the Roman Space Telescope promises to be a powerful tool for scientists and astronomers alike.
As preparations continue for the telescope’s launch, the scientific community eagerly anticipates the wealth of data and discoveries that the Roman Space Telescope will bring to light. This mission represents not only a leap forward in space exploration but also a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge.
Stay tuned for more updates on NASA’s Roman Space Telescope and its groundbreaking mission to explore the universe.