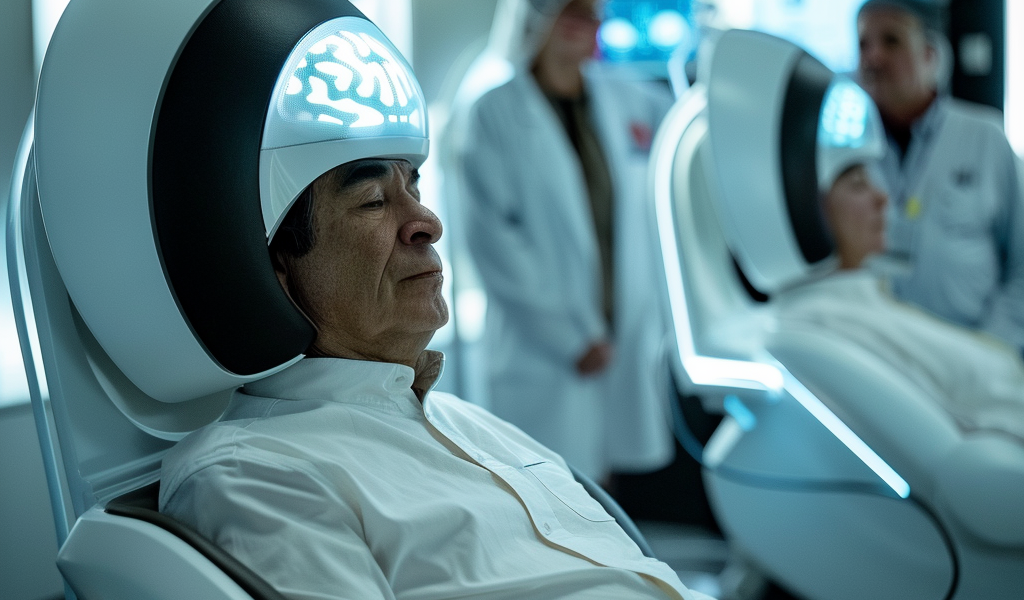
Recent advancements in medical technology have sparked interest in the potential of ultrasound waves to combat addiction. Researchers are exploring a groundbreaking $1 million device that resembles a helmet, designed to emit high-frequency ultrasound waves targeting a specific region of the brain associated with reward, motivation, and addiction behaviors.
This innovative approach aims to alter the brain’s response to addictive substances and behaviors, providing a non-invasive treatment option for individuals struggling with addiction. The concept revolves around the idea that by using ultrasound to stimulate the brain, it may be possible to recalibrate the neural pathways that contribute to addictive impulses.
The device operates by delivering focused ultrasound waves to the brain, which can penetrate the skull without causing damage. This technique is known as transcranial ultrasound stimulation (TUS). It is hypothesized that TUS can modulate neuronal activity in targeted areas, potentially diminishing the cravings and compulsions associated with addiction.
Initial studies have shown promise, suggesting that ultrasound stimulation can lead to significant changes in brain activity patterns linked to addiction. By influencing the brain’s reward system, researchers hope to create a therapeutic effect that aids in recovery and reduces relapse rates among individuals in treatment.
Furthermore, the non-invasive nature of this treatment could make it a more appealing option for patients compared to traditional methods, such as pharmacotherapy or intensive behavioral therapies. The helmet-like device could be used in various settings, including outpatient clinics and rehabilitation centers, offering flexibility in treatment delivery.
The research team behind this project is committed to conducting further studies to establish the efficacy and safety of this ultrasound-based treatment. They aim to gather comprehensive data on how the device affects brain function and behavior in individuals with different types of addiction, including substance use disorders and behavioral addictions.
As the medical community continues to seek innovative solutions for addiction treatment, this ultrasound technology represents a significant step forward. It aligns with the growing trend of utilizing precision medicine approaches, which tailor treatments to individual patients based on their unique biological and psychological profiles.
In addition to its potential applications in addiction treatment, the ultrasound device could also pave the way for new therapies for other mental health conditions. Researchers are exploring its use in treating anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), further expanding the scope of this promising technology.
While the concept of using ultrasound for brain stimulation is still in its early stages, the implications for addiction treatment are profound. If successful, this approach could revolutionize how addiction is treated, providing a safe and effective alternative to existing therapies.
The ongoing research and development of this ultrasound device highlight the importance of innovation in the field of mental health and addiction treatment. As scientists continue to explore the intricacies of the brain and its response to external stimuli, new avenues for healing and recovery are emerging.
In conclusion, the potential of ultrasound technology in treating addiction offers hope for many individuals seeking recovery. As research progresses, the medical community remains optimistic about the future of addiction treatment and the role that innovative technologies can play in improving patient outcomes.