Health Risks Associated with Burning Incense for Allergy and Asthma Sufferers
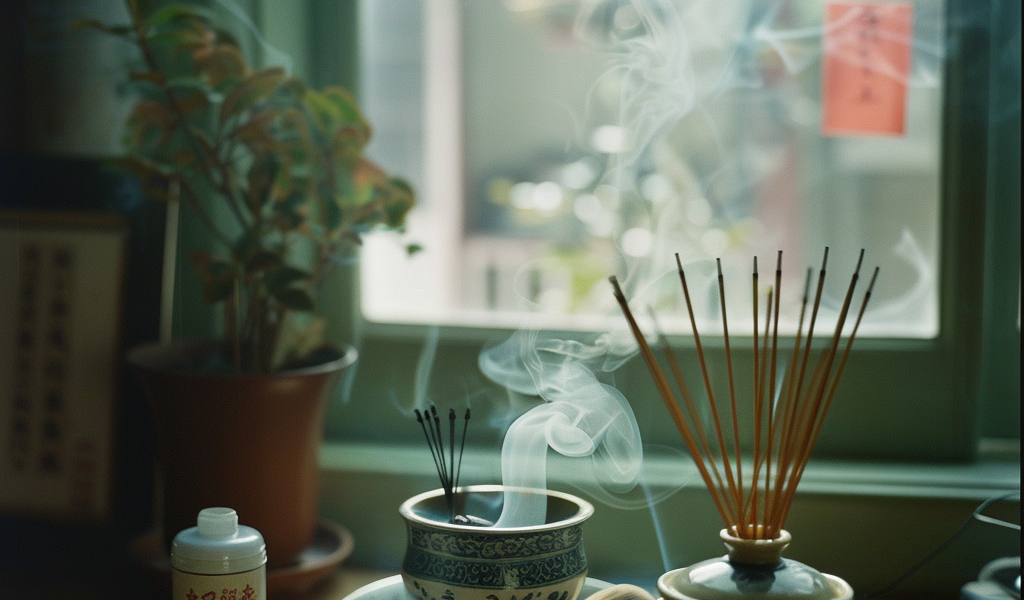
BOSTON (October 24, 2024) – Burning incense is a common practice in various cultures, often used during religious ceremonies, celebrations, and meditative practices. However, recent findings presented at the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting highlight significant health risks associated with this practice, particularly for individuals with allergies and asthma.
Dr. Gomeo Lam, the lead author of the study, shared a case involving an 87-year-old woman with a history of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who experienced unexplained shortness of breath. Upon further investigation, it was revealed that the patient burned incense daily as a way to honor her ancestors. Despite recommendations to cease this practice, the patient was reluctant to stop. Ultimately, the introduction of electric incense devices led to noticeable improvements in her respiratory symptoms.
The research emphasizes that burning incense can lead to various health issues, including:
- Headaches
- Respiratory dysfunction
- Dermatologic sensitivity
- Allergic reactions
Incense smoke contains harmful substances such as carbon, sulfur, nitrogen oxides, and formaldehyde, along with other carcinogenic compounds. The particulate matter produced from burning incense is significantly higher than that produced by cigarettes, with 45 mg generated per gram burned compared to just 10 mg from cigarettes.
Moreover, allergist Mary Lee-Wong, the senior author of the study, pointed out that secondhand smoke from incense can pose health risks to family members, including children. Similar to tobacco smoke, thirdhand incense smoke can linger on furniture, clothing, and various surfaces, potentially affecting individuals for months after the incense has been burned.
In addition to the health implications, the authors of the study noted that incense burning contributes to air pollution and poses a fire hazard. When advising patients who regularly burn incense, healthcare practitioners are encouraged to acknowledge the cultural significance of this practice. However, it is equally important to address the associated health risks.
To mitigate the negative effects of incense burning, healthcare professionals can suggest alternative practices, including:
- Using electric incense devices or aromatic vapors
- Implementing improved ventilation in the home
- Limiting the duration of incense burning
- Exploring simulated visuals that honor cultural traditions without the use of smoke
The ongoing research on incense burning and its health effects underscores the need for increased awareness among those who practice this cultural tradition. As the ACAAI Annual Scientific Meeting continues from October 24-28, more insights and studies will be shared regarding allergies, asthma, and other related health issues.
For individuals seeking more information about allergies and asthma, or to find an allergist nearby, resources are available through dedicated health organizations.