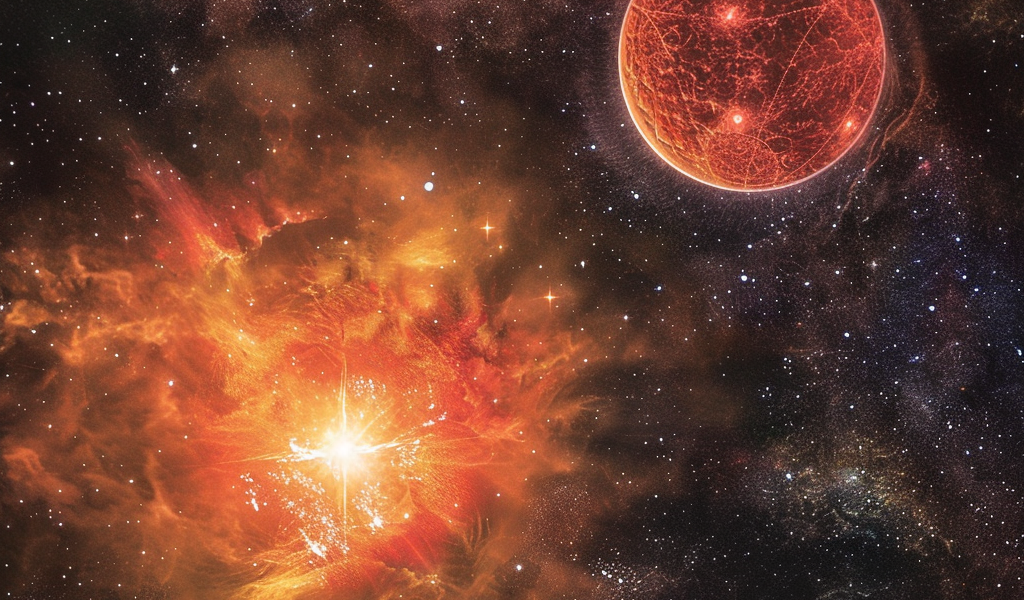
The enigmatic star Betelgeuse, one of the most prominent celestial objects visible in the night sky, is at the center of a fascinating new study that challenges previous assumptions about its imminent fate. Traditionally regarded as a potential candidate for a supernova explosion, recent findings suggest that the star’s dramatic fluctuations in brightness might be attributed to the influence of a companion star, rather affectionately dubbed the “Betelbuddy.” This discovery has been made by researchers from the Flatiron Institute, who have conducted extensive simulations to explore the dynamics of Betelgeuse and its cosmic companion.
Betelgeuse, formally known as Alpha Orionis, ranks as the tenth-brightest star in our night sky and is classified as a red giant. With a luminosity approximately 100,000 times that of our sun and a volume over 400 million times greater, Betelgeuse is nearing the end of its life cycle. When it eventually exhausts its nuclear fuel, it will undergo a spectacular explosion, potentially illuminating the daytime sky for weeks.
For years, astronomers have observed Betelgeuse’s peculiar behavior, characterized by cycles of brightening and dimming that have led to speculation about its stability and future. These changes in brightness have been likened to a heartbeat, with two distinct pulsation periods: one occurring over a little more than a year and another on a six-year cycle. The longer cycle has raised concerns that Betelgeuse could be on the verge of a catastrophic event.
However, the recent research led by astrophysicist Jared Goldberg and his colleagues has introduced a new perspective. By meticulously ruling out various intrinsic sources of variability, the team concluded that the most plausible explanation for the observed brightness changes is the presence of a companion star orbiting Betelgeuse. This unseen companion, which the researchers have playfully named the “Betelbuddy,” behaves like a cosmic snowplow, periodically sweeping away light-blocking dust in its orbit, thereby causing Betelgeuse to appear brighter at times.
Goldberg, a research fellow at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Astrophysics, emphasized the significance of this finding, stating, “We ruled out every intrinsic source of variability that we could think of as to why the brightening and dimming was happening in this way. The only hypothesis that seemed to fit is that Betelgeuse has a companion.” This revelation not only reshapes our understanding of Betelgeuse’s behavior but also highlights the intricate interactions between stars in binary systems.
The study involved collaboration with experts Meridith Joyce from the University of Wyoming and László Molnár from the Konkoly Observatory in Hungary. Together, they presented their findings in a paper accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal, contributing to the ongoing dialogue in the astronomical community about the nature of variable stars.
Understanding Betelgeuse’s variability is crucial for astronomers as they seek to predict the timing of its eventual demise. The two pulsation periods observed in Betelgeuse serve as vital indicators of its internal processes. If the longer pulsation cycle is indeed the star’s fundamental mode, this could imply that Betelgeuse is closer to its end than previously thought. Conversely, if the shorter cycle is the fundamental mode, then the longer cycle may represent a phenomenon known as a long secondary period, suggesting that the star’s death is still some time away.
As researchers continue to unravel the mysteries surrounding Betelgeuse and its newfound companion, the implications of this study extend beyond just one star. It opens the door to a deeper understanding of stellar evolution, binary star interactions, and the life cycles of massive stars. The dynamic nature of Betelgeuse, coupled with the potential influence of the Betelbuddy, underscores the complexity of the cosmos and the ongoing quest for knowledge that drives astronomers to explore the universe.
In summary, the latest research on Betelgeuse provides a fresh perspective on the behavior of this iconic star, suggesting that its variability may be linked to the presence of a companion star rather than an impending supernova. As scientists delve deeper into the data, the story of Betelgeuse continues to unfold, revealing the intricate dance of celestial bodies and the mysteries that lie within our vast universe.