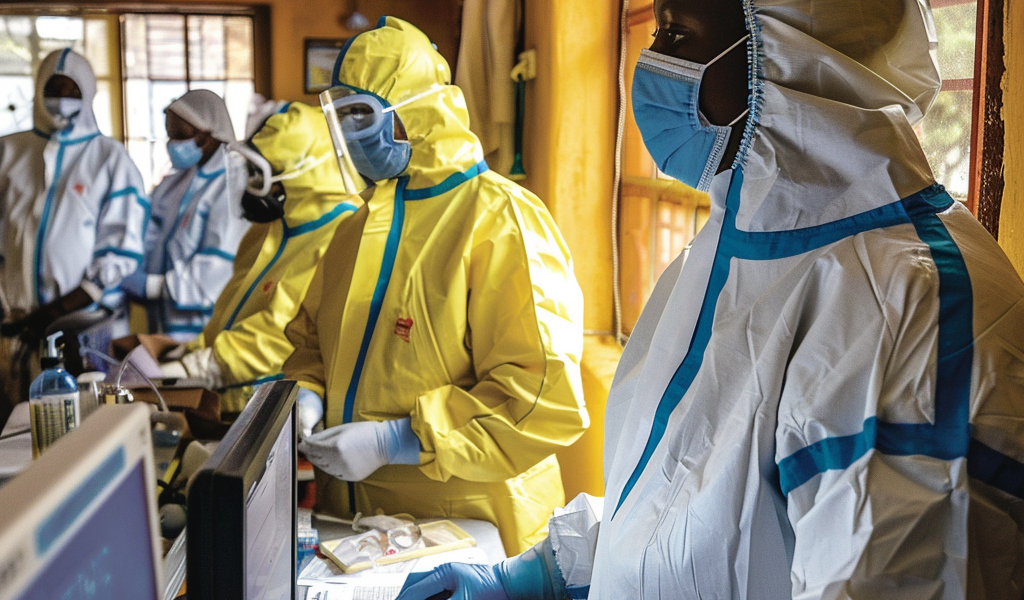
Rwanda is currently facing a serious health crisis as six individuals have succumbed to the Marburg virus, according to an announcement by the country’s health minister, Sabin Nsanzimana. The outbreak has raised alarm bells within the healthcare community, particularly as most of the deceased were healthcare workers from the intensive care unit.
Since the outbreak was officially confirmed on Friday, a total of twenty cases have been reported. The Marburg virus, which has a staggering fatality rate of up to 88%, belongs to the same family of viruses as Ebola. The virus is known to spread to humans from fruit bats, and it can be transmitted through direct contact with the bodily fluids of infected individuals.
Symptoms of the Marburg virus are severe and can include high fever, intense muscle pains, diarrhea, and vomiting. In extreme cases, the virus can lead to death through significant blood loss. Currently, there are no specific treatments or vaccines available for the Marburg virus, but various blood products, drugs, and immune therapies are under development, as noted by the World Health Organization (WHO).
In response to this outbreak, Rwandan authorities are ramping up efforts to contain the spread of the virus. This includes intensified contact tracing, surveillance, and testing protocols. Health officials are urging the public to remain vigilant, emphasizing the importance of hygiene practices such as washing hands with clean water and soap or using hand sanitizers. Additionally, citizens are encouraged to report any suspected cases of the virus to health authorities promptly.
This outbreak in Rwanda is not an isolated incident; neighboring Tanzania experienced a similar outbreak earlier in 2023. Furthermore, Uganda reported three deaths linked to the Marburg virus in 2017, highlighting the persistent threat posed by this disease in the region.
As the situation continues to develop, health officials and the government are working tirelessly to mitigate the impact of the virus and protect the health of the population. The global health community remains on alert, monitoring the situation closely as efforts to contain the outbreak unfold.
Public awareness and education about the Marburg virus are crucial in preventing further transmission. The government is likely to implement additional measures as needed, including public health campaigns aimed at informing citizens about the risks associated with the virus and the importance of seeking medical attention for any symptoms that may arise.
In the face of this outbreak, the resilience and cooperation of the Rwandan people will play a vital role in overcoming the challenges posed by the Marburg virus. As health officials work to control the spread, the international community is also watching closely, ready to provide support and assistance as necessary.