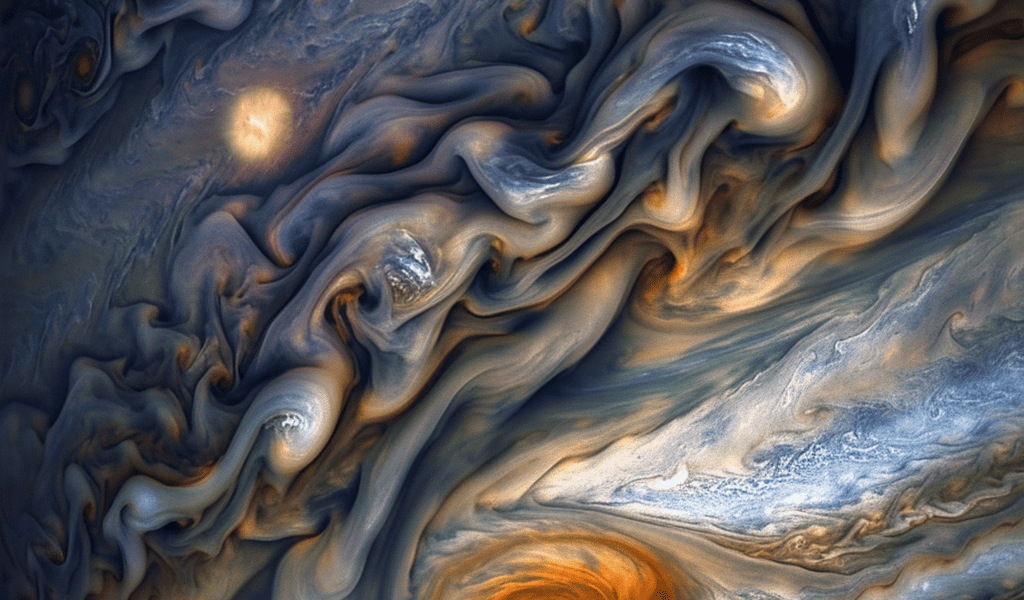
A stunning close-up image of Jupiter’s swirling clouds has been making waves on social media, with claims that it is the ‘closest ever taken’ of the gas giant. The image, captured by Junocam during perijove 26, has sparked awe and wonder among space enthusiasts and casual observers alike.
While the exact source of the claim regarding the image being the closest ever taken remains unclear, the SETI Institute has confirmed that the photo was indeed taken during a close approach of the Juno spacecraft to Jupiter. Perijove refers to the point in the orbit where a spacecraft is closest to the planet, allowing for the capture of breathtaking images just a few thousand kilometers from the cloud tops.
It’s worth noting that Juno has been consistently delivering remarkable images of Jupiter since it commenced its mission in 2016. The spacecraft has conducted multiple flybys, with the most recent one occurring on February 3, 2024. The closest flyby to date took place on August 27, 2016, when Juno came within 4,200 kilometers (2,600 miles) of Jupiter’s North pole, providing an up-close look at the mesmerizing gas giant’s swirling clouds.
Notably, this recent image is just one of many that showcase the stunning beauty of Jupiter. Other captivating shots of the planet include a video created by Kevin M. Gill using Cassini images, featuring the moons Io and Europa orbiting Jupiter. Despite their breathtaking appearance, Gill clarified that the motion depicted in the video was embellished for aesthetic purposes, with Io appearing to orbit slower than Europa due to the spacecraft’s velocity.
These extraordinary images serve as a reminder of the awe-inspiring wonders present in our solar system, offering a glimpse into the breathtaking beauty of celestial bodies like Jupiter. As space exploration continues to captivate the world, the allure of these mesmerizing images only grows stronger, igniting a sense of wonder and curiosity about the mysteries of the cosmos.