Study Forecasts Dramatic Increase in Chronic Liver Disease Due to Rising Obesity and Diabetes Rates
A study forecasts a dramatic increase in chronic liver disease, particularly metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosic liver disease (MASLD), over the next 25 years due to rising obesity and diabetes rates. This is expected to double liver cancer cases and triple liver transplant needs by 2050, emphasizing the need for increased awareness and early intervention.
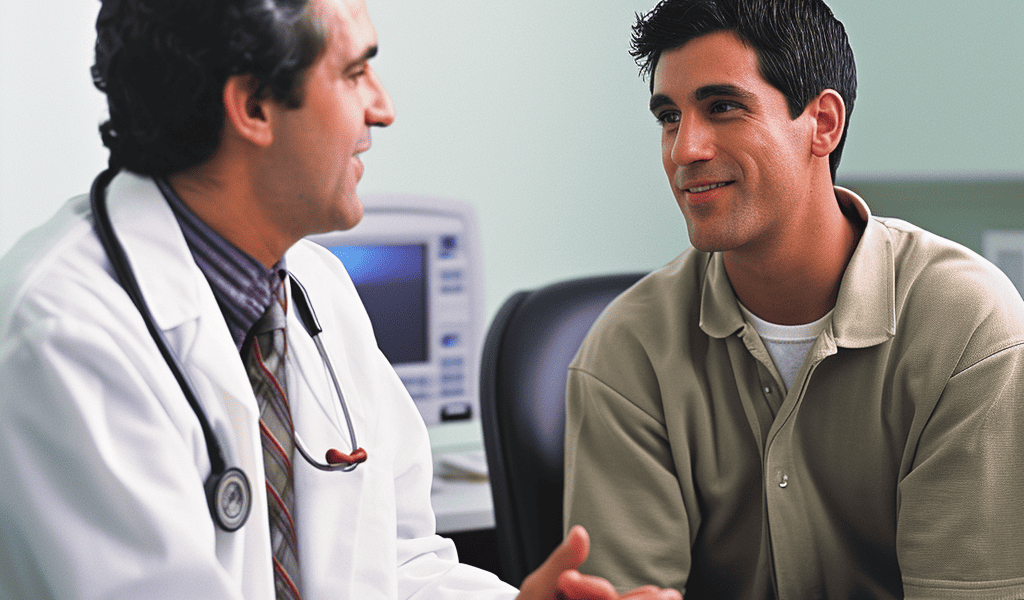
Liver doctors are altering their communication approach regarding liver disease due to the rise in cases.
The prevalence of the most prevalent type of chronic liver disease is projected to increase continuously over the next quarter-century. This escalation will place a substantial strain on healthcare systems, with forecasts indicating a near doubling of liver cancer cases and a near tripling in the demand for liver transplants by 2050. These findings are part of a study recently presented at The Liver Meeting, organized by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Rising rates of obesity and diabetes are blamed for the anticipated increase in the prevalence of the disease currently known as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease or MASLD — a label that was recently updated by medical organizations around the world to reduce the stigma associated with the previous name, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and to better describe common causes of the condition, which affects more than 30% of the global population.
Liver Transplantation Trends
“With diabetes and obesity rates on the rise, MASLD is expected to become the leading reason for liver transplants in the U.S.,” said Phuc Le, Ph.D., MPH, assistant professor at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine and lead researcher on the study, which created a mathematical model that anticipated annual population trends and the incidence and progression of MASLD. Hepatitis C is currently the most common cause of liver disease, followed by damage caused by long-term alcohol use.
Le’s model predicts a 23% rise in MASLD among adults in the U.S., affecting 27.8%. adults in 2020 and climbing to 34.3% by 2050. The most severe form of the disease is also e