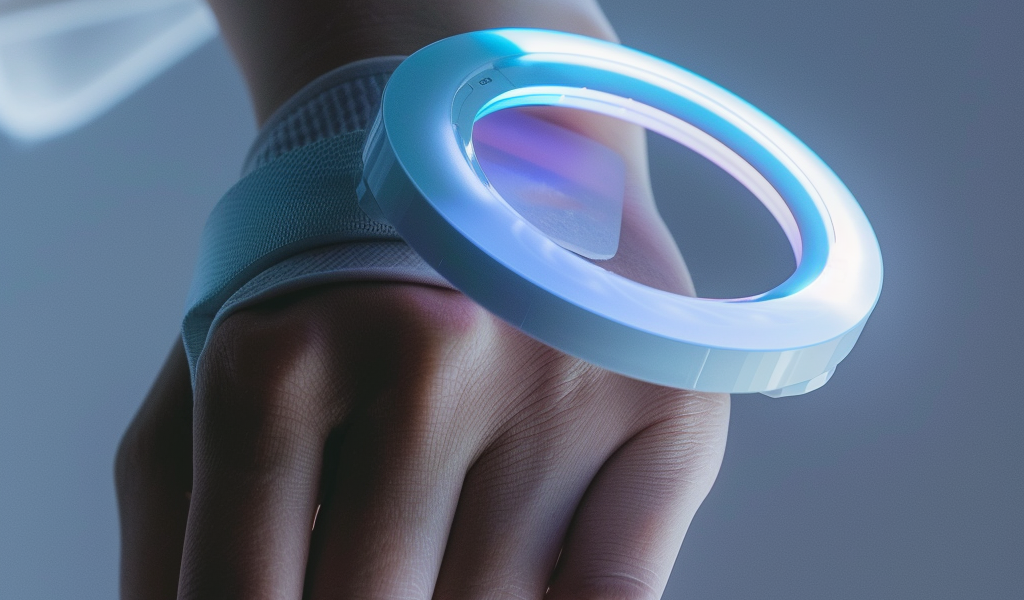
High blood pressure, a prevalent risk factor for mortality globally, affects one in every two adults, with only a quarter of those individuals having their blood pressure adequately managed. In a recent study conducted by Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a novel cuffless blood pressure monitoring device utilizing optical sensors was evaluated for its efficiency in continuously recording blood pressure without disrupting the patient.
The research, published in Frontiers in Medicine, showcases the potential of cuffless devices in revolutionizing the diagnosis, risk assessment, and treatment of hypertension. Dr. Naomi Fisher, the corresponding author of the study and a member of the Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Hypertension at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, emphasized the importance of easy and reliable blood pressure measurements outside traditional clinical settings for successful hypertension management.
With medical guidelines increasingly advocating for at-home blood pressure monitoring to enhance hypertension care, cuffless devices offer a solution to the limitations of traditional blood pressure cuffs. These devices provide a higher frequency of readings throughout the day and night, aiding in confirming hypertension diagnoses and guiding medication adjustments.
The concept of time-in-target-range (TTR) has emerged as a valuable metric for cardiovascular risk assessment, indicating the frequency of blood pressure readings within the normal range. However, obtaining frequent TTR measurements with conventional cuffs can be inconvenient and uncomfortable for patients. The study, led by Dr. Fisher in collaboration with Aktiia SA, a Swiss biotechnology company, analyzed data from over 5,000 participants in Europe and the U.K. who wore the Aktiia cuffless wrist monitor.
On average, the Aktiia device collected an impressive 29 blood pressure readings per day, offering a significant improvement in monitoring capabilities compared to traditional methods. The study’s findings suggest that cuffless devices could play a vital role in enhancing hypertension management by providing a more comprehensive and continuous assessment of blood pressure levels.