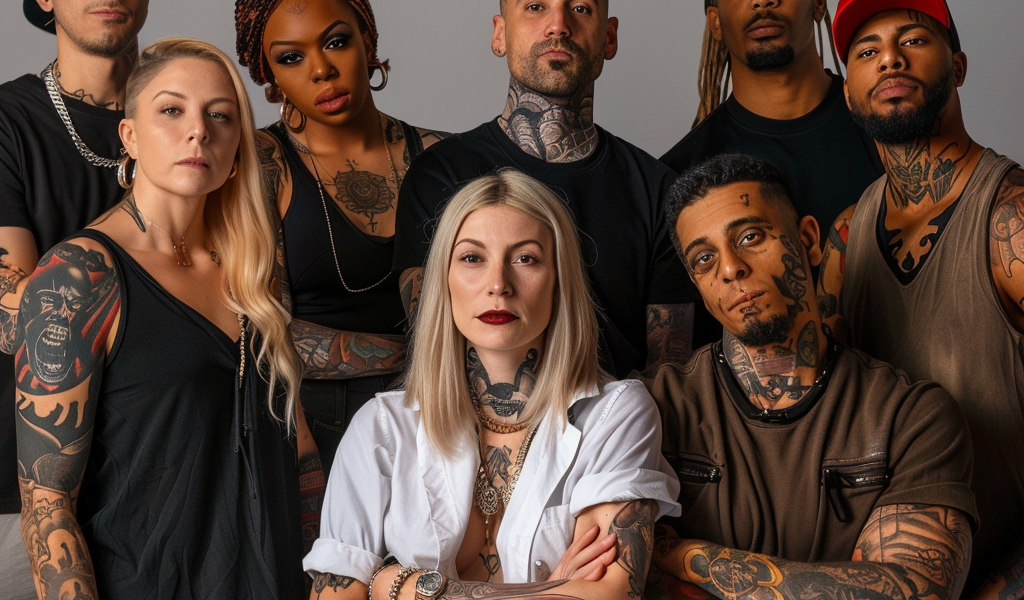
Having a tattoo increases the risk of developing cancer by 21%, according to a recent study. The researchers emphasize that they are not discouraging people from getting tattoos but are focused on ensuring the safety of the procedure.
Tattoos have become increasingly popular over the years, with 32% of US adults having at least one tattoo and 22% having multiple tattoos. The societal acceptance of tattoos has grown, with individuals from various backgrounds, including celebrities and politicians, proudly displaying their ink.
However, alongside the surge in tattoo popularity, there has been a rise in the incidence of malignant lymphoma, a type of cancer affecting the lymphatic system. Researchers at Lund University in Sweden conducted a study to explore the potential link between tattoos and lymphoma.
The study, led by Christel Nielsen, an associate professor of epidemiology at Lund University, involved individuals diagnosed with lymphoma who were compared to a control group without the condition. Participants were surveyed about their lifestyle choices, including whether they had tattoos.
The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in the body’s immune response and maintaining fluid balance. Lymphoma comprises non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and Hodgkin lymphoma, with NHL being the most common type. There are various subtypes of NHL, each with different growth rates and spread patterns, making it a prevalent cancer in the US.
The research included 11,905 Swedish individuals, with 2,938 having lymphoma. The study revealed that 21% of those with lymphoma had tattoos, compared to 18% of the control group without the condition.
After adjusting for factors like smoking and age, the researchers found a 21% higher risk of developing lymphoma among individuals with tattoos. The study suggests a potential association between tattoos and lymphoma, although further research is needed to confirm these findings.
Contrary to initial expectations, the size of the tattoo did not impact the risk of lymphoma, indicating that the risk is present regardless of tattoo size. Ongoing research aims to delve deeper into this connection between tattoos and cancer.