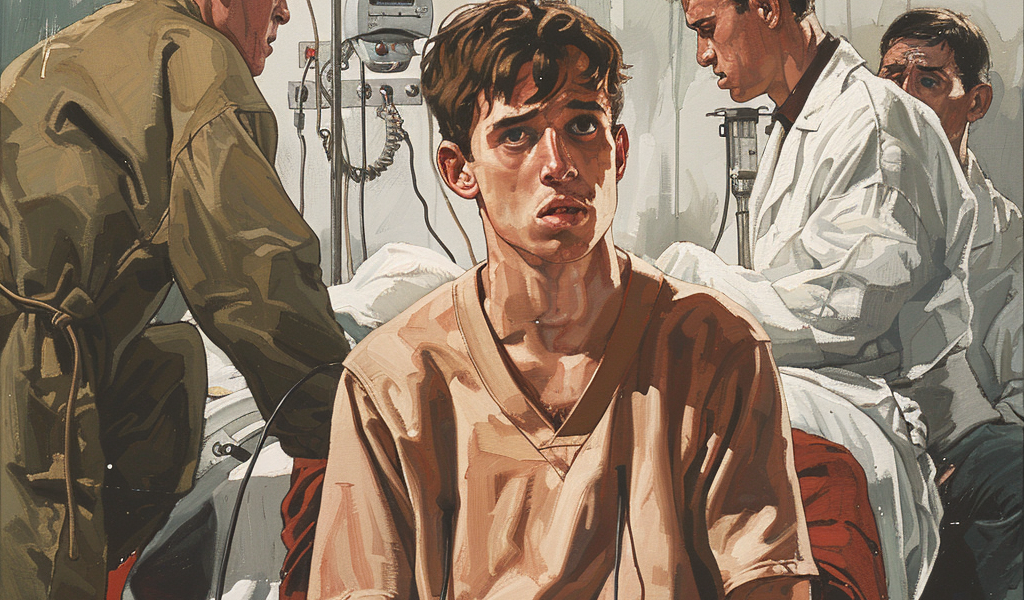
A startling incident in Connecticut has brought to light the potential dangers associated with smoking cannabis through unconventional means. A 25-year-old man found himself on the brink of death after using a cannabis bong filled with water from a garden hose, leading to a rare and deadly lung infection.
The individual, whose identity remains undisclosed, experienced alarming symptoms such as a ‘crackling’ noise in his lungs, followed by days of intense coughing, confusion, vomiting, and back pain. Upon seeking medical attention, urine tests confirmed that he had contracted Legionnaires’ disease, a severe bacterial infection notorious for causing lung damage and severe pneumonia.
It was revealed that the man, who had a history of substance abuse involving cannabis and alcohol, had also developed sepsis, a life-threatening immune response that claims a life in the United States every 90 seconds. This harrowing account emerged shortly after the Drug Enforcement Administration’s decision to reclassify marijuana as a Schedule III drug, indicating a perception of reduced harm compared to previous classifications.
Legionnaires’ disease, caused by the Legionella bacteria commonly found in freshwater environments like lakes and streams, can also thrive in human-made water systems such as showerheads, faucets, hot tubs, and plumbing systems if not adequately maintained. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlight that water contaminated with Legionella can form droplets that are then inhaled by individuals, leading to infection.
In the case of the Connecticut man, doctors noted his delirium, uncooperativeness, elevated heart rate, high blood pressure, and increased white blood cell count. Furthermore, the patient was diagnosed with emphysema, a condition that impairs the function of the lung’s air sacs, known as alveoli.
This incident serves as a cautionary tale regarding the potential risks associated with using contaminated water sources in devices like bongs for substance consumption. It underscores the importance of understanding and mitigating the dangers posed by bacterial infections like Legionnaires’ disease, particularly in the context of recreational drug use.