Precision Nutrition for Long-COVID Patients
A review article in the npj Science of Food journal discusses the potential of precision nutrition to address metabolic reprogramming and dysregulation in long-COVID patients caused by the SARS‐CoV‐2 virus. The article highlights the impact of the virus on human metabolic pathways, immune dysfunction, and redox imbalance, as well as the persistent symptoms experienced by long COVID patients. It emphasizes the importance of precision nutrition in managing and treating long-term COVID-19 symptoms.
Study Shows Physical Activity Reduces Risk of Chronic Pain
A recent Norwegian study found that physical activity significantly reduces the risk of chronic pain, with more active participants showing lower likelihood of developing widespread or severe pains. Even minimal physical activity showed a noticeable decrease in pain risk, with no apparent plateau in effectiveness as activity levels increased. The study did not specifically examine the risk of pain among the most active participants, indicating potential benefits of physical activity at intense levels. Further research is needed to explore potential genetic differences influencing susceptibility to pain.
Groundbreaking Study Shows Early High-Efficacy Therapies Improve Outcomes for Pediatric MS
Groundbreaking global study reveals that early and aggressive treatment with high-efficacy therapies can significantly improve outcomes for children with multiple sclerosis (MS). Research emphasizes the importance of administering high-efficacy disease-modifying therapies to pediatric MS patients early in their diagnosis to prevent the onset of significant disability. Study analyzed data from over 5,000 individuals diagnosed with MS during childhood over the past 30 years, drawing from international registries and national databases. Findings offer hope for improved treatment strategies for pediatric MS, potentially reshaping the approach to managing the condition in young patients.
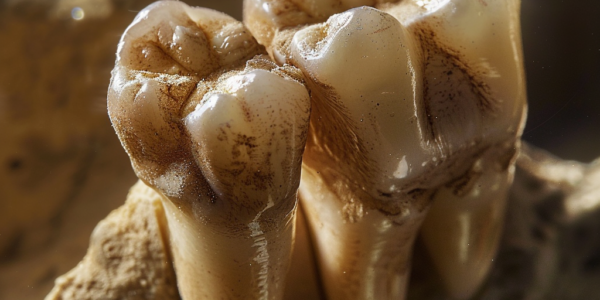
Ancient teeth reveal abundance of bacteria causing tooth decay and gum disease
Discovery of ancient teeth with high levels of cavity-causing bacteria sheds light on the impact of diet changes over the past 4,000 years. The rare find in Ireland’s County Limerick suggests that the prevalence of cavities today may be linked to the consumption of refined sugar and processed foods, which were not part of the ancient human diet.
Addressing the High Risk of Stroke in Children with Sickle Cell Disease in Sub-Saharan Africa
Sickle cell disease is a prevalent health issue in sub-Saharan Africa, where resources for treatment and screening are scarce. Without proper screening and treatment, the mortality rate for young children is alarmingly high. The lack of resources for screening in sub-Saharan Africa highlights the urgent need for affordable stroke-risk screening to save the lives of children with sickle cell disease.
Comprehensive Review of ADHD Treatments in Children and Adolescents
A recent study published in Pediatrics reviewed treatment options for ADHD in children and adolescents, identifying effective interventions and highlighting the growing availability of treatments. The study assessed various medications, including traditional stimulants and nonstimulants, as well as behavioral ADHD therapies. The findings emphasize the need for a comprehensive approach to effectively manage ADHD symptoms in young individuals.
Misinformation Continues to Plague Public Discourse Four Years into COVID-19 Pandemic
Four years after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, misinformation continues to plague public discourse, with a shift in focus towards vaccine-related conspiracy theories. False claims linking COVID-19 symptoms to 5G wireless technology, untested treatments, and even denial of the virus’s existence contributed to the spread of misinformation. PolitiFact has conducted over 2,000 fact checks specifically related to COVID vaccines. It is crucial to remain vigilant against the spread of misinformation, particularly concerning public health measures and vaccination efforts.
Study Reveals Lingering Impact of Tuskegee Syphilis Study on Black Americans’ COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake
A recent study by the University of Georgia reveals the lingering impact of the Tuskegee Syphilis Study on Black Americans’ willingness to receive the COVID-19 vaccine. Lead author Xiaolong ‘Chris’ Hou highlighted the concerning findings, emphasizing the need to address historical injustices that contribute to persistent health disparities. The study’s findings underscore the enduring impact of historical events on healthcare behaviors and the importance of addressing underlying factors perpetuating disparities in vaccine uptake.
Gender Differences in Dementia: Sex-Specific Blood Markers Linked to Memory Decline
Recent research has identified sex-specific blood biomarkers linked to memory decline, shedding light on potential early predictors of cognitive decline in middle-aged adults. The study, conducted by researchers at the Framingham Heart Study, analyzed a wide range of blood biomarkers to identify potential early warning signs of cognitive decline and found significant associations between certain biomarkers and memory changes in men and women. This discovery could lead to targeted interventions and personalized treatment strategies for cognitive decline, ultimately improving outcomes for individuals at risk of dementia.
New Tool Predicts and Safeguards Cancer Patients from Chemotherapy-Induced Kidney Damage
Researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital have developed an innovative tool to predict and safeguard cancer patients from chemotherapy-induced kidney damage. The tool, developed in collaboration with researchers from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and other institutions, utilizes patient data from six major U.S. cancer centers, making it the largest and first generalizable study of its kind. Cisplatin, a widely used chemotherapy drug, is highly effective in treating cancer but can also cause kidney injury, potentially leading to the discontinuation of life-saving cancer treatments. The newly developed risk prediction model aims to identify patients at the highest risk of moderate-to-severe kidney injury after receiving cisplatin. According to the researchers, the highest-risk patients had as much as a 20-fold higher risk of developing kidney injury after cisplatin compared to those in the lowest-risk group.